Great article from PoliceMag.com, originally posted HERE.
 Since its introduction nearly a decade ago, big data in the form of analytics has helped police agencies all over the world enhance decision making, improve strategies to combat crime, and ultimately solve—and prevent—more crimes. But while the benefits of mining and critically analyzing huge amounts of data are being realized in other developed countries from the United Kingdom to Canada to New Zealand, U.S. law enforcement agencies have generally been slower to jump on the bandwagon.
Since its introduction nearly a decade ago, big data in the form of analytics has helped police agencies all over the world enhance decision making, improve strategies to combat crime, and ultimately solve—and prevent—more crimes. But while the benefits of mining and critically analyzing huge amounts of data are being realized in other developed countries from the United Kingdom to Canada to New Zealand, U.S. law enforcement agencies have generally been slower to jump on the bandwagon.
The reasons for slower adoption of big data tools in the United States are as varied as the nearly 18,000 state and local law enforcement agencies around the country. For many, the decision to buy or not to buy advanced crime analytics software often comes down to the usual culprit: lack of money. With few exceptions, police agencies across the country are faced with the prospect of doing more with less. And with increased pressure on local departments to put more feet on the street, do more in terms of community policing, and divert funding to equip all officers with body cams, it’s often hard for departments to make big data solutions a top priority.
Money, however, is not the only issue slowing analytics adoption in the U.S. Unlike countries such as the U.K., the American law enforcement community is decentralized. It does not have a single system of data, standards, and operations. Rather, police departments here pride themselves on their individuality and independence. Walk into a meeting where 10 different departments are represented and you will likely see 10 different colors of uniforms.
The same holds true when it comes to information sharing. While it is often assumed that police departments all work in close cooperation with each other, the reality may be quite different.
 None of this is news, nor is it a criticism of U.S. police departments. It simply reflects Americans’ independent nature and the way in which law enforcement in this country is structured. It’s the thing that makes us great but, in the case of analytics, it’s also a major factor slowing analytics adoption.
None of this is news, nor is it a criticism of U.S. police departments. It simply reflects Americans’ independent nature and the way in which law enforcement in this country is structured. It’s the thing that makes us great but, in the case of analytics, it’s also a major factor slowing analytics adoption.
Big data adoption is also hampered by the sheer size of the U.S. Sure, from a pure geographic standpoint, the U.S. and Canada are similar in size. But most of Canada’s people live in Ontario or on the West Coast, near Vancouver. There are just over 200 police departments in all of Canada. Compare that to the U.S., where there are huge differences in the make-up of the population, not to mention lifestyle, attitudes, and so much more between, say, the Southwest and the Northeast.
Law enforcement policy-makers on the East Coast don’t know what to make of their counterparts on the West Coast and vice versa. Similarly, the day-to-day needs and demands placed on a police chief in Kansas City can’t help but be very different from those of his or her peers in Chicago, Los Angeles, Seattle, or Philadelphia.
 All of these factors have contributed to slowing the adoption of analytics by U.S. police agencies. They are also complicated by perhaps the most intangible impediment: fear of technology. Whether they like to admit it or not, some law enforcement leaders are more comfortable taking an “old school” approach to police work. They prefer business as usual, which means feet on the street and files stacked on their detectives’ desks, not sleek, state-of-the-art technology.
All of these factors have contributed to slowing the adoption of analytics by U.S. police agencies. They are also complicated by perhaps the most intangible impediment: fear of technology. Whether they like to admit it or not, some law enforcement leaders are more comfortable taking an “old school” approach to police work. They prefer business as usual, which means feet on the street and files stacked on their detectives’ desks, not sleek, state-of-the-art technology.
Change is never easy, especially when tried-and-true policing methods have proven to be effective. Decentralization also plays a part here – it’s easier to take technology risks when it’s mandated from above and much harder for the nearly 18,000 law enforcement chiefs in the U.S. to each take a step into the unknown. Nevertheless, change is coming, spurred in large part by the fact that the cost of advanced crime analytics is coming down.
Also easing the impact of costs to local agencies will be the dollars for big data solutions coming from the federal government. Those funds come with a catch, however, that gets at another obstacle. A significant portion of federal funds in the future will be earmarked for supporting regional initiatives. That means to be eligible for federal funds, many departments will have no choice but to work with their colleagues across jurisdictional boundaries. And while that may bring some initial resistance, regional cooperation will inevitably help to promote not just data sharing, but overall effectiveness.
 The public is also demanding increased police effectiveness and efficiency. Responding to that pressure, police chiefs are recognizing that big data solutions can have a huge impact on reducing the number of man-hours it takes to sift through mountains of data in order to solve crimes. This is particularly important as law enforcement finds itself confronting not only the standard array of home break-ins, car thefts, and the like, but also the threat of “lone wolf” terrorist attacks, cybercrime, and highly sophisticated international trafficking rings.
The public is also demanding increased police effectiveness and efficiency. Responding to that pressure, police chiefs are recognizing that big data solutions can have a huge impact on reducing the number of man-hours it takes to sift through mountains of data in order to solve crimes. This is particularly important as law enforcement finds itself confronting not only the standard array of home break-ins, car thefts, and the like, but also the threat of “lone wolf” terrorist attacks, cybercrime, and highly sophisticated international trafficking rings.
Fortunately, as analytics software has become more affordable, it has also become easier to use. No longer the exclusive domain of the IT department, newer big data solutions are now designed to be used by front line analysts and investigators, with just one or two days of training and without the need for sophisticated oversight.
This has dramatically changed the role of law enforcement analysts. Formerly the department statistician, today’s analyst has become a critically important member of the crime fighting team, capable of rapidly moving from tactical analysis to the focal point of providing intelligence on high-profile crimes and strategic crime-fighting initiatives.
Ease of use also comes into play as a new generation of officers, many of whom were raised on Google and Xbox, begin to take on leadership roles in their departments. These individuals are used to having the latest technology at their immediate disposal. They will readily see that a big data solution can not only play a critical role in more effective policing, but also pay for itself in savings of both time and money.
 The growing use of cloud computing plays a role in this equation. Storing data in the cloud is becoming accepted as safe and secure, bringing with it economic advantages and removing the need for departments to provide highly specialized IT staff and infrastructure previously required to support analytical solutions.
The growing use of cloud computing plays a role in this equation. Storing data in the cloud is becoming accepted as safe and secure, bringing with it economic advantages and removing the need for departments to provide highly specialized IT staff and infrastructure previously required to support analytical solutions.
All of these factors are combining to change the face of effective policing in the U.S. That will mean significantly greater acceptance of analytics to mine everything from social media files, emails, text messages, and the content of police RMS systems to phone records, license plate reader data, and ballistics data. Efficiencies of scale will dictate greater cooperation among departments, resulting in increased efficiency and more effective policing. Being able to quickly search and find critical information in data that police agencies already have in hand will undoubtedly improve decision making and officer safety, while helping to solve cases more quickly.
 Crime Tech Solutions, who earlier this year acquired TN based Case Closed Software, delivers unique value to customers with comprehensive investigative case management software, sophisticated link analysis tools, criminal intelligence management software, and crime mapping technology that includes some of the industry’s best analytics and reporting capabilities.
Crime Tech Solutions, who earlier this year acquired TN based Case Closed Software, delivers unique value to customers with comprehensive investigative case management software, sophisticated link analysis tools, criminal intelligence management software, and crime mapping technology that includes some of the industry’s best analytics and reporting capabilities.
Tag Archives: police software
Overland Park senior crime analyst Jamie May joins Crime Tech Solutions
September 16, 2016 – (Leander, TX) Crime Tech Solutions, a fast-growing provider of low cost / high performance crime fighting software and analytics is delighted to announce the addition of Jamie May as senior analyst and strategic advisor to the company.
 Ms. May has spent over 17 years as a crime and intelligence analyst for Overland Park Police Department in Kansas, and is a recognized expert in crime analysis, mapping, and criminal intelligence. She has sat on critical crime analysis committees including the International Association of Crime Analysts’ Ethics Committee (IACA) and is a past Vice President / Secretary at Mid American Regional Crime Analyst Network (MARCAN).
Ms. May has spent over 17 years as a crime and intelligence analyst for Overland Park Police Department in Kansas, and is a recognized expert in crime analysis, mapping, and criminal intelligence. She has sat on critical crime analysis committees including the International Association of Crime Analysts’ Ethics Committee (IACA) and is a past Vice President / Secretary at Mid American Regional Crime Analyst Network (MARCAN).
“Jamie brings an incredible amount of user experience and innovation to the company”, said Kevin Konczal, Crime Tech Solutions’ VP of Sales. “She’s been active in this community for years, and co-authored the ground-breaking guide, GIS in Law Enforcement: Implementation Issues and Case Studies.”
“To me, Crime Tech Solutions represents a truly innovative company that understands how to develop and market very good technology at prices that most agencies can actually afford”, said Ms. May. “I’m looking forward to being part of the continued growth here.”
In her role with the company, Ms. May will interact with customers and prospects to help align the company’s solution strategy with market and user requirements.
 Crime Tech Solutions, who earlier this year acquired TN based Case Closed Software, delivers unique value to customers with comprehensive investigative case management software, sophisticated link analysis tools, criminal intelligence management software, and crime mapping technology that includes some of the industry’s best analytics and reporting capabilities.
Crime Tech Solutions, who earlier this year acquired TN based Case Closed Software, delivers unique value to customers with comprehensive investigative case management software, sophisticated link analysis tools, criminal intelligence management software, and crime mapping technology that includes some of the industry’s best analytics and reporting capabilities.
Using crime analysis solutions to take a ‘Byte’ out of crime
 Posted by Crime Tech Solutions
Posted by Crime Tech Solutions
Law enforcement agencies everywhere are tasked with reducing and investigating crime with fewer and fewer resources at their disposal. “To protect and serve” is the highest responsibilities one can sign up for, particularly in light of recent well-publicized criticisms of police by activists in every city.
That responsibility weighs even heavier in a world with no shortage of criminals and terrorists. There’s never enough money in the budget to adequately deal with all of the issues that face an individual agency on a daily basis. Never enough feet on the street, as they say.
New Tools for Age-Old Problems
Perhaps that’s why agencies everywhere are moving to fight crime with an evolving 21st century weapon – law enforcement software including investigative case management, link and social network analysis, and, importantly, crime analytics with geospatial and temporal mapping.

Crime analytics and investigation software have proven themselves to be valuable tools in thwarting criminal activity by helping to better define resource allocation, target investigations more accurately, and enhancing public safety,
According to some reports, law enforcement budgets have been reduced by over 80% since the early 2000s. Still, agencies are asked to do more and more, with less and less.
Analytics in Policing

Analytics in law enforcement play a key role in helping law enforcement agencies better forecast what types of crimes are most likely to occur in a certain area within a certain window of time. While no predictive analytics solution offers the clarity of a crystal ball, they can be effective in affecting crime reduction and public safety.
Predictive analysis, in essence, is taking data from disparate sources, analyzing them and then using the results to anticipate, prevent and respond more effectively to future crime. Those disparate data sources typically include historical crime data from records management systems, calls for service/dispatch information, tip lines, confidential informant information, and specialized criminal intelligence data.
The Five W’s of Predictive Analytics
Within this disparate data lie the 5 W’s of information that can be used by crime analysis software to build predictions. Those key pieces include:
- Arrest records – who committed crimes
- Geospatial data – where crimes have occurred
- Temporal data – when crimes have occurred
- Statistical data – what crimes have occurred
- Investigation data – why (and how) the crimes occurred
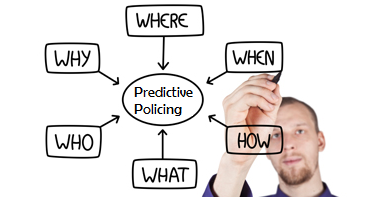
Using the 5 W’s, agencies are able to gain insight and make predictions about likely future criminal behavior. For example, if a certain type of crime (what) tends to occur in ‘this’ area (where) at ‘this’ time (when), and by ‘this’ type of individual (who) for ‘this’ reason (why)… it would be wise to deploy resources in that area at that time in order to prevent the incidents from ever occurring. This, of course, is a dramatic over-simplification of the types of analytics that make up predictive policing, but illustrates the general concept well.
Although criminals will always try to be one step ahead of the law, agencies deploying predictive analytics are able to maximize the effectiveness of its staff and other resources, increasing public safety, and keeping bad guys off the street.
More about Crime Tech Solutions
Crime Tech Solutions is an Austin, TX based provider of crime and fraud analytics software for commercial and law enforcement groups. Our offerings include sophisticated Case Closed™ investigative case management and major case management, GangBuster™ gang intelligence software, powerful link analysis software, evidence management, mobile applications for law enforcement, comprehensive crime analytics with mapping and temporal reporting, and 28 CFR Part 23 compliant criminal intelligence database management systems.
Crime Tech Solutions’ continued growth fuels management team expansion
September 13, 2016 – (Leander, TX) Crime Tech Solutions, a fast-growing provider of low cost crime fighting software and analytics today announced the appointment of Kevin Konczal as Vice President of Sales. The company created the position in response to rapid growth in market share for crime analysis and investigative case management software.
 Mr. Konczal is a seasoned start-up and marketing expert with over 30 years of diversified business management, marketing and start-up experience in information technology and consumer goods. Additionally, Konczal has over two decades of Public Safety service as a police officer, Deputy Sheriff and Special Agent.
Mr. Konczal is a seasoned start-up and marketing expert with over 30 years of diversified business management, marketing and start-up experience in information technology and consumer goods. Additionally, Konczal has over two decades of Public Safety service as a police officer, Deputy Sheriff and Special Agent.
Most recently, he held the position as a Regional Sales Manager for TriTech Software Systems, a leading provider of public safety software.
“Kevin is a seasoned executive with a combination of public service and information technology expertise”, said Crime Tech Solutions’ chief technology officer Keith Weigand. “The management team is looking forward to adding his leadership within the sales organization.”
In addition to his executive career, Konczal serves on several advisory boards, commissions and boards of directors. He attended Oakland College studying Criminal Justice and completed the Dallas Police Academy. Notably, he was awarded the Police Commendation Award for saving the lives of fellow officers in a deadly force c onfrontation.
onfrontation.
“The exciting thing about Crime Tech Solutions”, added Konczal “is their clear position as a fast-growing company dedicated to low price and high performance software for law enforcement.”
“I’m looking forward to working with a company that delivers true value to customers with comprehensive investigative case management software, sophisticated link analysis tools, criminal intelligence management software, and crime mapping technology that includes what I think are the industry’s best analytics and reporting capabilities”, he added.
Earlier this year, Crime Tech Solutions acquired Tennessee based Case Closed Software (www.caseclosedsoftware.com).
About Crime Tech Solutions
Crime Tech Solutions (www.crimetechsolutions.com) is a fast-growing U.S. based provider of low cost / high performance investigation software and crime analytics. The company proudly supports the International Association of Crime Analysts (www.iaca.net), International Association of Chiefs of Police (www.iacp.org), the National Sheriff’s Association (www.sheriffs.org), and the association of Law Enforcement Intelligence Units (www.leiu.org).
The company’s products include Case Closed investigative case management software, link and social network analytics, 28 CFR Part 23 compliant criminal intelligence management software, enterprise search for law enforcement, and crime analytics with mapping, reporting, and predictive policing.
Data continues to influence policing
Great article by Megan Favignano at New Press Now. Original article at http://www.newspressnow.com/news/local_news/data-continues-to-influence-policing/article_ef968ba2-389c-5289-b341-a9818ae231d7.html
A copy of the article follows:
 A recent report questions how some police departments are using data to forecast future crimes.
A recent report questions how some police departments are using data to forecast future crimes.
The report examined how departments are utilizing predictive policing, a computer software that uses data to forecast where crime may happen, who may commit it and who could be potential victims.
Upturn, an analysis organization out of Washington, D.C., that works with a variety of groups, published the report “Stuck in a Pattern” last month. “Predictive policing,” the report states, is a marketing term popularized by vendors who sell the software.
 How police departments nationwide utilize crime statistics and the software available to patrol officers monitoring incidents has evolved a lot in the past couple decades, Sgt. Tracy Barton with the St. Joseph Police Department said. Barton started as a patrol officer 20 years ago. He said having software like police have today would have been useful.
How police departments nationwide utilize crime statistics and the software available to patrol officers monitoring incidents has evolved a lot in the past couple decades, Sgt. Tracy Barton with the St. Joseph Police Department said. Barton started as a patrol officer 20 years ago. He said having software like police have today would have been useful.
In the past, crime analysts used physical maps and mathematical algorithms to do what software does instantly today. Barton, the St. Joseph Police Department’s crime analyst, uses software that takes into account crimes reported to police to show crime hot spots in the city. A map of those hot spots is available online. Officers, he said, have access to a more in-depth version of that hot spots map, which includes extra details about the area and the crimes occurring.
The hot spots approach St. Joseph police use is most helpful in preventing crime when a series of crimes occur or when there is a crime pattern in a given area, he said. St. Joseph’s small size, Barton added, poses an extra challenge.

The St. Joseph Police Department has had its current software for just a few years. It doesn’t fit the definition of the predictive policing software Upturn outlines in the recent report. The software used locally depends on crime reports police receive. Predictive policing also looks at what types of business are located in an area, if repeat offenders live nearby and other information to predict where crimes may occur. Typically, according to the recent report, predictive policing takes one of two approaches, focusing either on place-based data or person-based data to make predictions.
Kevin Bryant, sociology and criminology professor at Benedictine College, said when people hear predictive policing described, they often think of the movie “Minority Report.” The software, he said, is nothing like in the movies.
“Predictive policing now has kind of morphed into better proactive methods that are based on prediction to some extent in forecasting risk,” Bryant said of how data-driven policing has changed over time. “But what we’ve learned through evaluation studies is that it’s really more important what the police do when they’re in a crime hot spot.”
 ryant worked with the Shawnee, Kansas, Police Department on research that looked at what he calls “smart policing.” In his research and in other work he has read, Bryant said it’s important for police to have a high visibility in crime hot spots, for officers to make connections with the public and for them to avoid staying in crime hot spots for extended periods of time.
ryant worked with the Shawnee, Kansas, Police Department on research that looked at what he calls “smart policing.” In his research and in other work he has read, Bryant said it’s important for police to have a high visibility in crime hot spots, for officers to make connections with the public and for them to avoid staying in crime hot spots for extended periods of time.When police are in a hot spot for too long, public surveys show area residents feel like they are being picked on rather than protected, he said. Predictive policing takes into account businesses in a given area. Bryant said some types of facilities are at a higher risk of victimization and others can attract crime to an area.
“Knowing where bars, taverns, restaurants, gas stations, convenience stores are, we can actually use their locations as a means of forecasting where crime might emerge at a later date,” Bryant said. “Part of predictive policing is predicting who the risky offenders are and that can be controversial.”
Upturn’s report also explored an ongoing debate among criminologists on the impact of using crime reports when determining patrol.
“Criminologists have long emphasized that crime reports and other statistics gathered by the police are not an accurate record of the crime that happens in a community,” the report states.

Report: California 'Gang Intelligence Database' fails to ensure individual privacy
 Here is another great reason why it is important for agencies to follow best practices in intelligence data management. The regulations behind DOJ 28 CFR Part 23 are meant to help agencies walk the line between effective intelligence gathering and the right to an individual’s privacy.
Here is another great reason why it is important for agencies to follow best practices in intelligence data management. The regulations behind DOJ 28 CFR Part 23 are meant to help agencies walk the line between effective intelligence gathering and the right to an individual’s privacy.
28 CFR Part 23 compliant intelligence management software is available and an inexpensive way for agencies to walk the line between effective criminal intelligence and individual privacy.
SFGate writer Vivian Ho’s article is at http://www.sfgate.com/crime/article/Audit-Many-in-California-gang-database-listed-9137916.php
We think it is well-written and accurately describes a real problem faced by law enforcement agencies across the country.
Crime Tech Solutions is a low price / high performance innovator in crime analytics and law enforcement crime-fighting software. The clear price/performance leader for crime fighting software, the company’s offerings include sophisticated Case Closed™ investigative case management and major case management, GangBuster™ gang intelligence software, powerful link analysis software, evidence management, mobile applications for law enforcement, comprehensive crime analytics with mapping and predictive policing, and 28 CFR Part 23 compliant criminal intelligence database management systems.
Crime Tech Solutions Acquires Case Closed Software
June 1, 2016 (Austin, TX) Crime Tech Solutions, LLC, a leading provider of analytics and investigation software for law enforcement and commercial markets, today announced that it has acquired Cleveland, TN based Case Closed Software in a cash transaction. The terms of the deal were not released, but according to Crime Tech Solutions’ founder and president Douglas Wood, the acquisition brings together two dynamic and fast-growing software companies with an unparalleled complement of technologies.
“For Crime Tech Solutions, the opportunity to add Case Closed Software into the fold was too good to pass up” said Mr. Wood. “We think that the technology offered by Case Closed helps to further differentiate us in the market as the price performance leader for this type of investigative solution.”
Crime Tech Solutions, based in the city of Leander, TX, delivers advanced analytics and investigation software to commercial investigators and law enforcement agencies across the globe. Their solution suite includes criminal intelligence software, sophisticated crime analytics with geospatial mapping, and powerful link analysis and visualization software. The company says that the addition of Case Closed Software expands those offerings even further.
Case Closed Software develops and markets investigative case management software specifically designed for law enforcement agencies. The suite is built around four primary software products including best-in-class investigative case management software, property and evidence tracking, a gang database tool, and an integrated link analysis and data visualization tool. The company also plans to release the solution as Case Closed Cloud for cloud-based access.
“Case Closed couldn’t be happier than to be joining Crime Tech Solutions,” said Keith Weigand, the company’s founder. “The blending of our technologies creates a suite that will add tremendous value to our mutual customers, and will be hard for others to duplicate.”
According to both Mr. Weigand and Mr. Wood, the name Case Closed will continue on as the product brand, given its widespread popularity and loyal customer base. Crime Tech Solutions is expected to retain all Case Closed employees, with Mr. Weigand joining as the company’s chief technical officer.
Crime Tech Solutions says it expects continued growth via ongoing software sales and strategic acquisitions.
About Crime Tech Solutions
(NOTE: Crime Tech Solutions is an Austin, TX based provider of crime and fraud analytics software for commercial and law enforcement groups. Our offerings include sophisticated Case Closed™ investigative case management and major case management, GangBuster™ gang intelligence software, powerful link analysis software, evidence management, mobile applications for law enforcement, comprehensive crime analytics with mapping and predictive policing, and 28 CFR Part 23 compliant criminal intelligence database management systems.)
Is the Most Dangerous Company in America?
Posted by Tyler Wood, Operations Manager at Crime Tech Solutions
 This is a very interesting read about the current big data analytics darling, Palantir Technologies. The article from GS Early appears on the Personal Liberty website HERE.
This is a very interesting read about the current big data analytics darling, Palantir Technologies. The article from GS Early appears on the Personal Liberty website HERE.
The original article follows…
“I was reading my newsfeeds and I came across a very interesting story about this highly secretive company that is apparently buying up as much Palo Alto, California real estate as it can get its hands on.
But that isn’t even the most interesting thing about them. What piques my interest is how this start-up that just added another $450 million to its funding — it now has about $20 billion in funding — got its money.
The company is called Palantir Technologies. If the name sounds familiar, it’s because it comes from JRR Tolkein’s trilogy of fantasy novels. In The Fellowship of the Ring, Saruman the wizard uses the Palantir of Orthanc, an indestructible sphere of dark crystal, to see into the future and communicate across the world.
That sounds geeky and innocuous enough, no?
But Palantir the company’s biggest clients are the FBI, SEC and the CIA. It is a Big Data company that also has corporate clients, but much of the work — from what anyone can tell — comes from hush-hush projects for the U.S. intelligence community.
This crystal ball of a company sounds less like a quaint fantasy than a key element of the “thought police” in Philip K. Dick’s dark science fiction tale “The Minority Report.”
In “The Minority Report,” the police used computers to predict when and where a crime would occur and apprehend the perpetrator before he actually committed the crime.
The crazy thing is, we’re now living in a world where Big Data makes that possible.
First, let me explain what Big Data is. Basically, now that our lives are completely recorded in various media — traffic cameras, debit card transactions, loyalty cards, phone calls, television shows watched, internet, social media, SMS texts, etc. — computers are powerful enough now to sort through all this data from all these sources and come up with predictive patterns for individuals and groups.
This is a very hot area for retail stores. But it also has enormous implications in a variety of industries; and many of them are helpful.
It is certainly a tool that law enforcement and our intelligence services would find valuable to root out potential terrorists or groups that are planning some terrorist act. It is also useful to find people who are attempting to elude authorities. And being able to get ahead of the some of the more devious players on Wall Street and their illegal trading schemes would be nice.
But you can see where this could be turned on Americans, just as easily as the NSA turned its endeavors on to less than righteous paths.
Palantir is raising eyebrows in the epicenter of digital startups because most companies, once they reach a certain size, move out of Palo Alto and build a campus in some surrounding town.
Not Palantir. It now owns about 10-15 percent of all the available space in Palo Alto, more than 250,000 square feet. It is the fourth most valuable venture backed company in the world.
The irony in the article was, the concern wasn’t about its biggest client or what it’s doing for the CIA, it was the fact that it’s eating up all the available commercial space in Palo Alto and not leaving room for new startups.
My concern is a bit deeper. The CIA could have quietly gone to one of the major Big Data firms like Accenture or IBM and worked with them on whatever it is they needed. But instead they essentially built their own company, where there are much fewer people to throw up roadblocks to the work being done. I have no problem with government using Big Data to protect us; my concern is when intelligence and enforcement agencies have unfettered use of it.
But, there’s no turning back the clock. We are in the Big Data, cybersecurity age and plenty of these companies already exist. Usually their goal is help their clients sell more lavender soap in February or figure out what kind of salad greens a 37-year-old mother of two prefers to buy at 7 p.m. on a Wednesday evening.
On a fundamental level, it’s best to keep your digital footprint light. Make sure you have secure passwords that aren’t just 1234 or your pet’s name. Most browsers have an “incognito” mode that won’t track your browser history. But truth be told, if someone really wants your history, they can get it.
If you’re more serious about hiding your footprints, look into encrypted services like Tor (www.torproject.com) that will protect against traffic analysis (browser history, instant messaging, etc.). It’s free and very good.
Transactions in bitcoins is a way to keep your footprint light in the marketplace.
And if you’re looking to make money on the trend, there are any number of companies that are at the forefront of cybersecurity (Palo Alto Networks, FireEye, Synamtec) and Big Data (Accenture, IBM, Teradata, Oracle).
–GS Early“
(NOTE: Crime Tech Solutions is an Austin, TX based provider of crime and fraud analytics software for commercial and law enforcement groups. We proudly support the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners (ACFE), International Association of Chiefs of Police (IACP), Association of Law Enforcement Intelligence Units (LEIU) and International Association of Crime Analysts (IACA). Our offerings include sophisticated link analysis software, comprehensive crime mapping and predictive policing, and criminal intelligence database management systems.)
Link Analysis and Crime – An examination.
Posted by Tyler Wood, Operations Manager at Crime Tech Solutions
 The topic of fraud is widely discussed, and the focus of thousands upon thousands of articles. Television shows such as Crime, Inc and American Greed have become popular due, in part, to our fascination with the topic of fraud.
The topic of fraud is widely discussed, and the focus of thousands upon thousands of articles. Television shows such as Crime, Inc and American Greed have become popular due, in part, to our fascination with the topic of fraud.
The organizations that are affected by fraud are also fascinated… but for entirely different reasons. Some estimates suggest that the US economy loses 11 trillion dollars each year due to one form of fraud or another. It’s little wonder, therefore, that the companies most frequently defrauded have been heavily investing in anti-fraud technologies at an increasing rate over the past decade or more.
The biggest problem with fraud, of course, is that it is always evolving in a very Darwinian fashion. Like a living, breathing entity, fraud schemes change over time in order to survive. As the targets of fraud schemes put new policies, procedures and/or systems to deter the activities, the schemes modify and find new ways to survive.
So, since the nature of criminal activity is such that they constantly change, how do investigators find a fool proof methodology to ensure they are 100% safe from them? The answer, of course, is that they can’t. They never will; at least not until we live in a world such as the one depicted in the 2002 film Minority Report, starring Tom Cruise. In that movie, criminals are arrested prior to committing a crime based upon the predictions of psychics called ‘Precogs’. Corporations and individual targets of fraud can only wish.
Nope, there are no Precogs running around locking up would-be practitioners of fraud that would protect banks, insurance companies, Medicaid and Medicare programs, victims of Ponzi schemes, victims of identity theft, and countless others. Instead, organizations rely upon skilled knowledge workers using purpose-built crime and fraud analytics technology that can detect anomalies in patterns, suspicious transactions, hotspot mapping, networks of fraudsters, and other sophisticated data analytics tools.
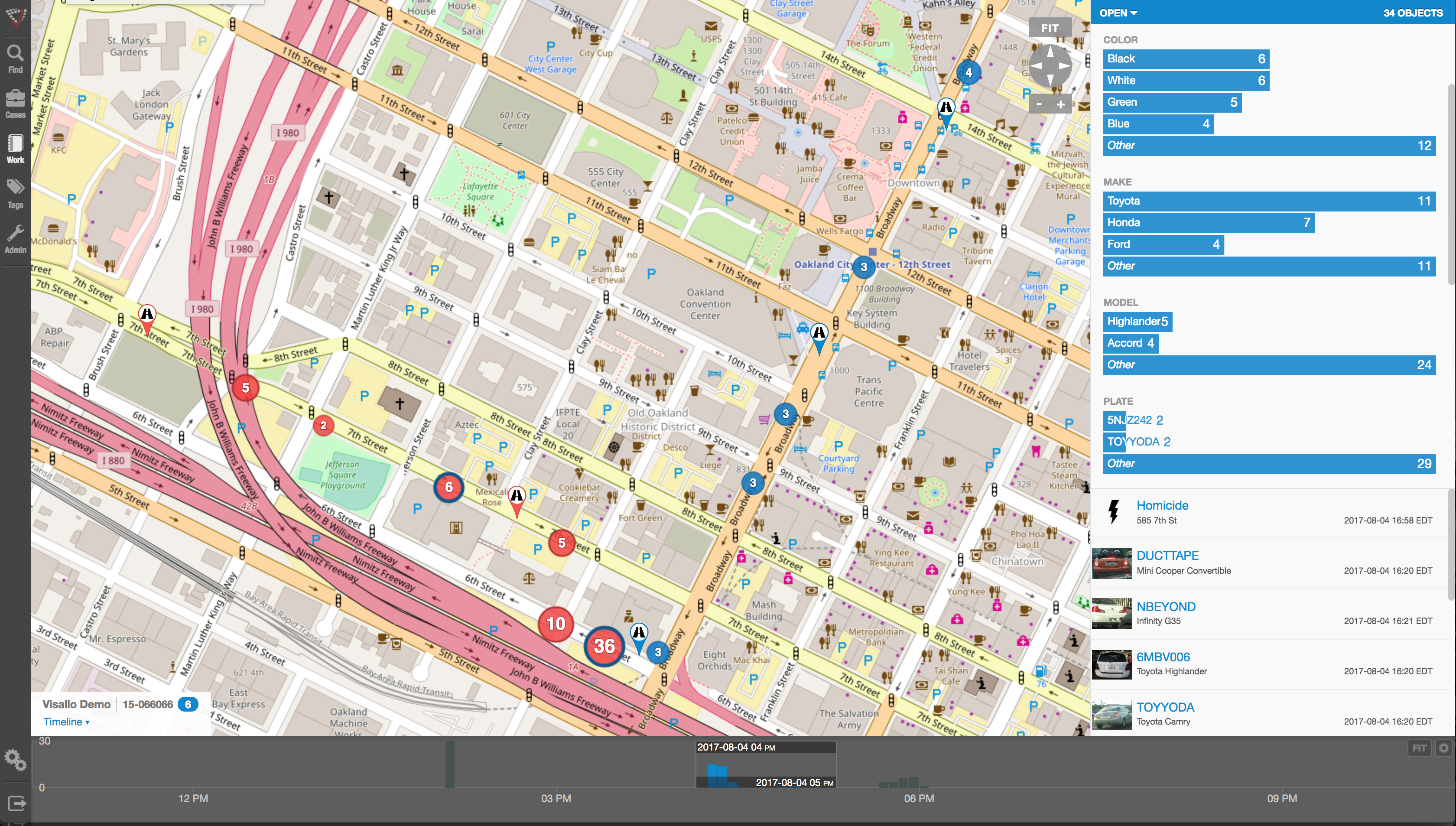
Crime and fraud analytics
Any discussion of analytics and investigation software must touch upon the topic of ‘big data’. No longer just a buzz word, big data literally fuels the insights gathered by organizations in every area of business. Naturally, then, organizations who have been traditionally targeted by fraudsters have increasingly invested in crime technology such as investigation software and analytics in order to exploit the phenomenon.
 Of course, big data in and by itself does nothing. It just sits there. Nobody has ever yelled “Help! We’ve been defrauded! Call the big data!” Big data is only useful when it can be transformed into ‘smart data’. In other words, understanding the big picture of costly fraudulent activities is not akin to understanding the specifics of ‘who’ is defrauding you, and ‘how’ they are doing it.
Of course, big data in and by itself does nothing. It just sits there. Nobody has ever yelled “Help! We’ve been defrauded! Call the big data!” Big data is only useful when it can be transformed into ‘smart data’. In other words, understanding the big picture of costly fraudulent activities is not akin to understanding the specifics of ‘who’ is defrauding you, and ‘how’ they are doing it.
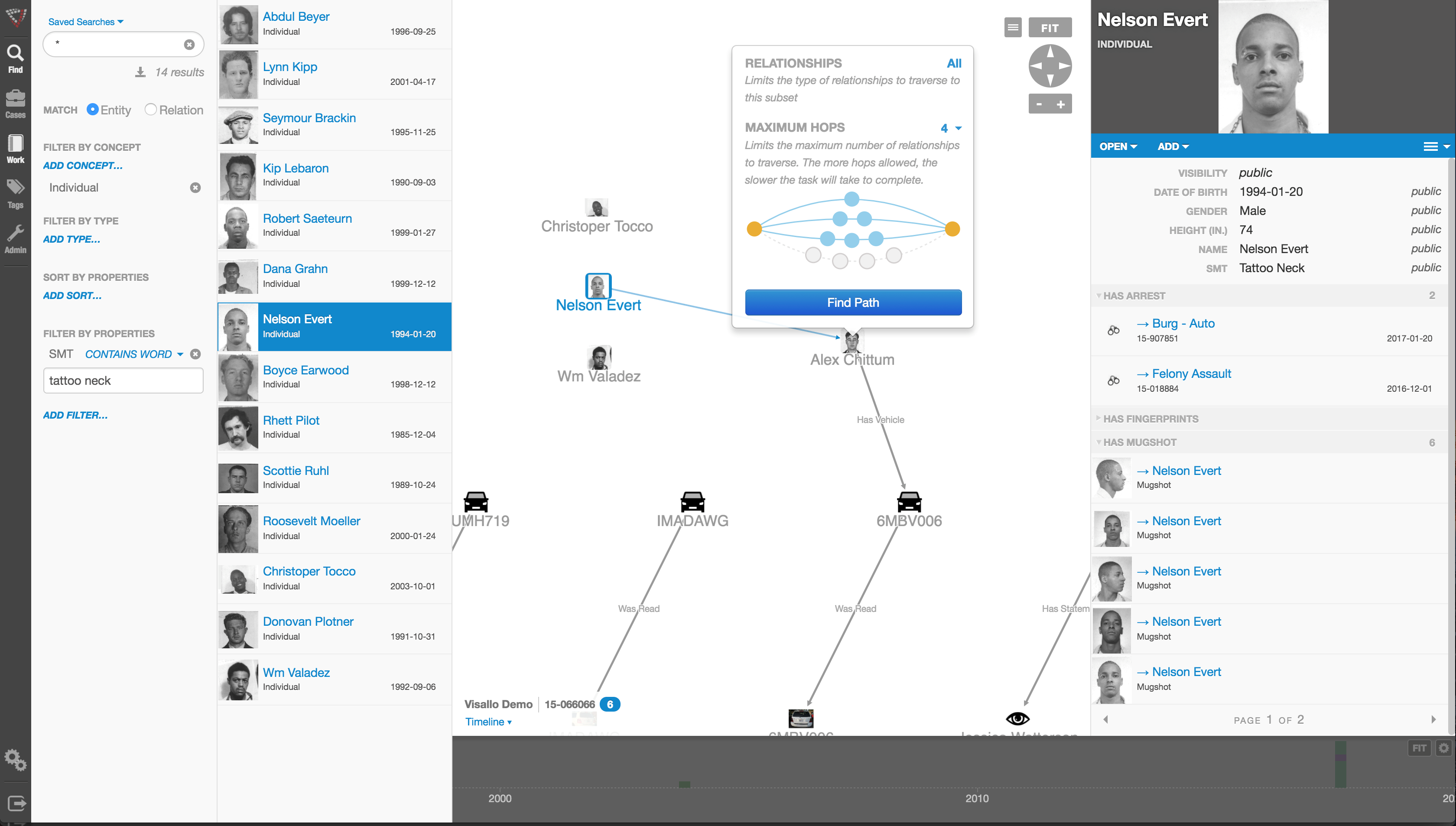
Those questions can best be answered through the powerful data mining and link analysis software tools offered by Austin, TX based Crime Tech Solutions in partnership with Sterling, VA based Visallo. Effective link analysis complements big data analytics platforms, helping to expose previously undetected fraud, and the entities (people or organizations) committing it.
Link Analysis – Transforming big data into smart data
By definition, link analysis is a data analysis technique that examines relationships among people, places, and things. As a visual tool, link analysis provides users a powerful method to quickly understand and ‘see’ what is happening. Because of this, it is widely used by financial institutions such as banks and insurance companies to uncover criminal networks, improve fraud investigations, detect insider fraud, and expose money laundering schemes. Similarly, government agencies use link analysis to investigate fraud, enhance screening processes, uncover terrorist networks and investigate criminal activities.
At Crime Tech Solutions, we liken the question of how to detect and deter fraud to ‘How do you eat an elephant?’ The answer, of course, is one bite at a time. If big data is the elephant, comprehensive link analysis software is part of the one ‘bite’ at a time. Or should we say ‘byte’.
(NOTE: Crime Tech Solutions is an Austin, TX based provider of investigation software and analytics for commercial and law enforcement groups. We proudly support the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners (ACFE), International Association of Chiefs of Police (IACP), Association of Law Enforcement Intelligence Units (LEIU) and International Association of Crime Analysts (IACA). Our offerings include sophisticated link analysis software, an industry-leading investigation case management solution, and criminal intelligence database management systems.)
What is Crime Analysis?
Posted by Tyler Wood Crime Tech Solutions, your source for investigation software.
The information provided on this page comes primarily from Boba, R. (2008: Pages 3 through 6) Crime Analysis with Crime Mapping. For a full discussion of the crime analysis discipline, refer to the book which can be obtained through www.sagepub.com.
Over the past 20 years, many scholars have developed definitions of crime analysis. Although definitions of crime analysis differ in specifics, they share several common components: all agree that crime analysis supports the mission of the police agency, utilizes systematic methods and information, and provides information to a range of audiences. Thus, the following definition of crime analysis is used as the foundation of this initiative:
Crime analysis is the systematic study of crime and disorder problems as well as other police–related issues—including sociodemographic, spatial, and temporal factors—to assist the police in criminal apprehension, crime and disorder reduction, crime prevention, and evaluation.
Clarification of each aspect of this definition helps to demonstrate the various elements of crime analysis. Generally, to study means to inquire into, investigate, examine closely, and/or scrutinize information. Crime analysis, then, is the focused and systematic examination of crime and disorder problems as well as other police-related issues. Crime analysis is not haphazard or anecdotal; rather, it involves the application of social science data collection procedures, analytical methods, and statistical techniques.
More specifically, crime analysis employs both qualitative and quantitative data and methods. Crime analysts use qualitative data and methods when they examine non-numerical data for the purpose of discovering underlying meanings and patterns of relationships. The qualitative methods specific to crime analysis include field research (such as observing characteristics of locations) and content analysis (such as examining police report narratives). Crime analysts use quantitative data and methods when they conduct statistical analysis of numerical or categorical data. Although much of the work in crime analysis is quantitative, crime analysts use simple statistical methods, such as frequencies, percentages, means, and rates. Typical crime analysis tools include link analysis and crime mapping software.
The central focus of crime analysis is the study of crime (e.g., rape, robbery, and burglary); disorder problems (e.g., noise complaints, burglar alarms, and suspicious activity); and information related to the nature of incidents, offenders, and victims or targets of crime (targets refer to inanimate objects, such as buildings or property). Crime analysts also study other police-related operational issues, such as staffing needs and areas of police service. Even though this discipline is called crime analysis, it actually includes much more than just the examination of crime incidents.
Although many different characteristics of crime and disorder are relevant in crime analysis, the three most important kinds of information that crime analysts use are sociodemographic, spatial, and temporal. Sociodemographic information consists of the personal characteristics of individuals and groups, such as sex, race, income, age, and education. On an individual level, crime analysts use sociodemographic information to search for and identify crime suspects. On a broader level, they use such information to determine the characteristics of groups and how they relate to crime. For example, analysts may use sociodemographic information to answer the question, “Is there a white, male suspect, 30 to 35 years of age, with brown hair and brown eyes, to link to a particular robbery?” or “Can demographic characteristics explain why the people in one group are victimized more often than people in another group in a particular area?”
The spatial nature of crime and other police-related issues is central to understanding the nature of a problem. In recent years, improvements in computer technology and the availability of electronic data have facilitated a larger role for spatial analysis in crime analysis. Visual displays of crime locations (maps) and their relationship to other events and geographic features are essential to understanding the nature of crime and disorder. Recent developments in criminological theory have encouraged crime analysts to focus on geographic patterns of crime, by examining situations in which victims and offenders come together in time and space.
Finally, the temporal nature of crime, disorder, and other police-related issues is a major component of crime analysis. Crime analysts conduct several levels of temporal analysis, including (a) examination of long-term patterns in crime trends over several years, the seasonal nature of crime, and patterns by month; (b) examination of mid-length patterns, such as patterns by day of week and time of day; and (c) examination of short-term patterns, such as patterns by day of the week, time of day, or time between incidents within a particular crime series.
The final part of the crime analysis definition—”to assist the police in criminal apprehension, crime and disorder reduction, crime prevention, and evaluation” generally summarizes the purpose and goals of crime analysis. The primary purpose of crime analysis is to support (i.e., “assist”) the operations of a police department. Without police, crime analysis would not exist as it is defined here.
The first goal of crime analysis is to assist in criminal apprehension, given that this is a fundamental goal of the police. For instance, a detective may be investigating a robbery incident in which the perpetrator used a particular modus operandi (i.e., method of the crime). A crime analyst might assist the detective by searching a database of previous robberies for similar cases.
Another fundamental police goal is to prevent crime through methods other than apprehension. Thus, the second goal of crime analysis is to help identify and analyze crime and disorder problems as well as to develop crime prevention responses for those problems. For example, members of a police department may wish to conduct a residential burglary prevention campaign and would like to target their resources in areas with the largest residential burglary problem. A crime analyst can assist by conducting an analysis of residential burglary to examine how, when, and where the burglaries occurred along with which items were stolen. The analyst can then use this information to develop crime prevention suggestions, (such as closing and locking garage doors) for specific areas.
Many of the problems that police deal with or are asked to solve are not criminal in nature; rather, they are related to quality of life and disorder. Some examples include false burglar alarms, loud noise complaints, traffic control, and neighbor disputes. The third goal of crime analysis stems from the police objective to reduce crime and disorder. Crime analysts can assist police with these efforts by researching and analyzing problems such as suspicious activity, noise complaints, code violations, and trespass warnings. This research can provide officers with information they can use to address these issues before they become more serious criminal problems.
The final goal of crime analysis is to help with the evaluation of police efforts by determining the level of success of programs and initiatives implemented to control and prevent crime and disorder and measuring how effectively police organizations are run. In recent years, local police agencies have become increasingly interested in determining the effectiveness of their crime control and prevention programs and initiatives. For example, an evaluation might be conducted to determine the effectiveness of a two-month burglary surveillance or of a crime prevention program that has sought to implement crime prevention through environmental design (CPTED) principles within several apartment communities. Crime analysts also assist police departments in evaluating internal organizational procedures, such as resource allocation (i.e., how officers are assigned to patrol areas), realignment of geographic boundaries, the forecasting of staffing needs, and the development of performance measures. Police agencies keep such procedures under constant scrutiny in order to ensure that the agencies are running effectively.
In summary, the primary objective of crime analysis is to assist the police in reducing and preventing crime and disorder. Present cutting edge policing strategies, such as hotspots policing, problem-oriented policing, disorder policing, intelligence-led policing, and CompStat management strategies, are centered on directing crime prevention and crime reduction responses based on crime analysis results. Although crime analysis is recognized today as important by both the policing and the academic communities, it is a young discipline and is still being developed. Consequently, it is necessary to provide new and experienced crime analysts with training and assistance that improves their skills and provides them examples of best practices from around the country and the world. http://crimetechsolutions.com