(March 5, 2018) Austin, TX – Case Closed Software® announced today that one of the largest constitutional tax collectors in the state of Florida has selected Case Closed Cloud™ as its next-generation investigative case management platform.
 The county office serves approximately 1.5M residents, and is involved in the collection of taxes and the investigation of all related criminal cases. Through Case Closed Cloud, the agency will easily manage files and documents associated with individual cases and specific case actions.
The county office serves approximately 1.5M residents, and is involved in the collection of taxes and the investigation of all related criminal cases. Through Case Closed Cloud, the agency will easily manage files and documents associated with individual cases and specific case actions.
The agency acts an independent agency to be free from influence by local or state agencies that have the power to levy taxes, and serves the county as its agent for the administration of varying taxes.
“A unique feature of Case Closed Cloud is the ability for agencies to use their own forms in conjunction with the software”, said Douglas Wood, president of Case Closed Software. “The tax collector’s office will have full access to all of the materials they need, wherever they need them, through our cloud-based case management software”.
 Case Closed Cloud is an innovative new Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) investigation management platform from Crime Tech Solutions, LLC – a leading provider of software to law enforcement, state agencies, and other investigative agencies.
Case Closed Cloud is an innovative new Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) investigation management platform from Crime Tech Solutions, LLC – a leading provider of software to law enforcement, state agencies, and other investigative agencies.
“Case Close Cloud is an innovative new offering, and is already disrupting the case management industry”, said Douglas Wood, the company’s founder and chief executive. “This new customer chose us specifically for our unparalleled feature set, and because they can literally start using the system immediately without any internal IT headaches.”
Case Closed Software offers its software in both ‘on-premise’ and ‘cloud-based’ deployments, meaning that customers can quickly deploy the functionality in the manner that best suits their business requirements.
Category Archives: Financial Crimes
Link Analysis and Crime – An examination.
Posted by Tyler Wood, Operations Manager at Crime Tech Solutions
 The topic of fraud is widely discussed, and the focus of thousands upon thousands of articles. Television shows such as Crime, Inc and American Greed have become popular due, in part, to our fascination with the topic of fraud.
The topic of fraud is widely discussed, and the focus of thousands upon thousands of articles. Television shows such as Crime, Inc and American Greed have become popular due, in part, to our fascination with the topic of fraud.
The organizations that are affected by fraud are also fascinated… but for entirely different reasons. Some estimates suggest that the US economy loses 11 trillion dollars each year due to one form of fraud or another. It’s little wonder, therefore, that the companies most frequently defrauded have been heavily investing in anti-fraud technologies at an increasing rate over the past decade or more.
The biggest problem with fraud, of course, is that it is always evolving in a very Darwinian fashion. Like a living, breathing entity, fraud schemes change over time in order to survive. As the targets of fraud schemes put new policies, procedures and/or systems to deter the activities, the schemes modify and find new ways to survive.
So, since the nature of criminal activity is such that they constantly change, how do investigators find a fool proof methodology to ensure they are 100% safe from them? The answer, of course, is that they can’t. They never will; at least not until we live in a world such as the one depicted in the 2002 film Minority Report, starring Tom Cruise. In that movie, criminals are arrested prior to committing a crime based upon the predictions of psychics called ‘Precogs’. Corporations and individual targets of fraud can only wish.
Nope, there are no Precogs running around locking up would-be practitioners of fraud that would protect banks, insurance companies, Medicaid and Medicare programs, victims of Ponzi schemes, victims of identity theft, and countless others. Instead, organizations rely upon skilled knowledge workers using purpose-built crime and fraud analytics technology that can detect anomalies in patterns, suspicious transactions, hotspot mapping, networks of fraudsters, and other sophisticated data analytics tools.
Crime and fraud analytics
Any discussion of analytics and investigation software must touch upon the topic of ‘big data’. No longer just a buzz word, big data literally fuels the insights gathered by organizations in every area of business. Naturally, then, organizations who have been traditionally targeted by fraudsters have increasingly invested in crime technology such as investigation software and analytics in order to exploit the phenomenon.
 Of course, big data in and by itself does nothing. It just sits there. Nobody has ever yelled “Help! We’ve been defrauded! Call the big data!” Big data is only useful when it can be transformed into ‘smart data’. In other words, understanding the big picture of costly fraudulent activities is not akin to understanding the specifics of ‘who’ is defrauding you, and ‘how’ they are doing it.
Of course, big data in and by itself does nothing. It just sits there. Nobody has ever yelled “Help! We’ve been defrauded! Call the big data!” Big data is only useful when it can be transformed into ‘smart data’. In other words, understanding the big picture of costly fraudulent activities is not akin to understanding the specifics of ‘who’ is defrauding you, and ‘how’ they are doing it.
Those questions can best be answered through the powerful data mining and link analysis software tools offered by Austin, TX based Crime Tech Solutions in partnership with Sterling, VA based Visallo. Effective link analysis complements big data analytics platforms, helping to expose previously undetected fraud, and the entities (people or organizations) committing it.
Link Analysis – Transforming big data into smart data
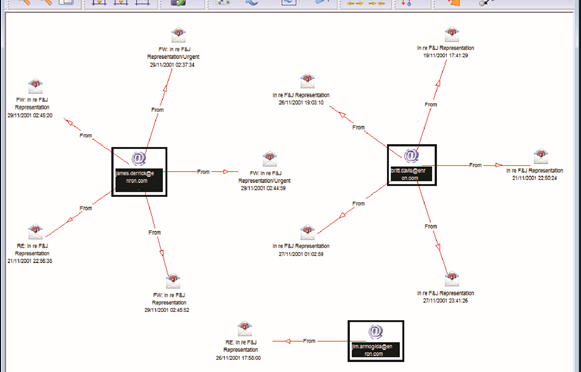
By definition, link analysis is a data analysis technique that examines relationships among people, places, and things. As a visual tool, link analysis provides users a powerful method to quickly understand and ‘see’ what is happening. Because of this, it is widely used by financial institutions such as banks and insurance companies to uncover criminal networks, improve fraud investigations, detect insider fraud, and expose money laundering schemes. Similarly, government agencies use link analysis to investigate fraud, enhance screening processes, uncover terrorist networks and investigate criminal activities.
At Crime Tech Solutions, we liken the question of how to detect and deter fraud to ‘How do you eat an elephant?’ The answer, of course, is one bite at a time. If big data is the elephant, comprehensive link analysis software is part of the one ‘bite’ at a time. Or should we say ‘byte’.
(NOTE: Crime Tech Solutions is an Austin, TX based provider of investigation software and analytics for commercial and law enforcement groups. We proudly support the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners (ACFE), International Association of Chiefs of Police (IACP), Association of Law Enforcement Intelligence Units (LEIU) and International Association of Crime Analysts (IACA). Our offerings include sophisticated link analysis software, an industry-leading investigation case management solution, and criminal intelligence database management systems.)
What is Link / Social Network Analysis?
Posted by Crime Tech Solutions
Some linkage data, such as telephone call detail records, may be simple but voluminous, with uniform node and link types and a great deal of regularity. Other data, such as law enforcement data, may be extremely rich and varied, though sparse, with elements possessing many attributes and confidence values that may change over time.
Various techniques are appropriate for distinct problems. For example, heuristic, localized methods might be appropriate for matching known patterns to a network of financial transactions in a criminal investigation. Efficient global search strategies, on the other hand, might be best for finding centrality or severability in a telephone network.
Link analysis can be broken down into two components—link generation, and utilization of the resulting linkage graph.
Link Generation
Link generation is the process of computing the links, link attributes and node attributes. There are several different ways to define links. The different approaches yield very different linkage graphs. A key aspect in defining a link analysis is deciding which representation to use.
Explicit Links
A link may be created between the nodes corresponding to each pair of entities in a transaction. For example, with a call detail record, a link is created between the originating telephone number and the destination telephone number. This is referred to as an explicit link.
Aggregate Links
A single link may be created from multiple transactions. For example, a single link could represent all telephone calls between two parties, and a link attribute might be the number of calls represented. Thus, several explicit links may be collapsed into a single aggregate link.
Inferred Relationships
Links may also be created between pairs of nodes based on inferred strengths of relationships between them. These are sometimes referred to as soft links, association links, or co-occurrence links. Classes of algorithms for these computations include association rules, Bayesian belief networks and context vectors. For example, a link may be created between any pair of nodes whose context vectors lie within a certain radius of one another. Typically, one attribute of such a link is the strength of the relationship it represents. Time is a key feature that offers an opportunity to uncover linkages that might be missed by more typical data analysis approaches. For example, suppose a temporal analysis of wire transfer records indicates that a transfer from account A to person X at one bank is temporally proximate to a transfer from account B to person Y at another bank. This yields an inferred link between accounts A and B. If other aspects of the accounts or transactions are also suspicious, they may be flagged for additional scrutiny for possible money laundering activity.
A specific instance of inferred relationships is identifying two nodes that may actually correspond to the same physical entity, such as a person or an account. Link analysis includes mechanisms for collapsing these to a single node. Typically, the analyst creates rules or selects parameters specifying in which instances to merge nodes in this fashion.
Utilization
Once a linkage graph, including the link and node attributes, has been defined, it can be browsed, searched or used to create variables as inputs to a decision system.
Visualization
In visualizing linking graphs, each node is represented as an icon, and each link is represented as a line or an arrow between two nodes. The node and link attributes may be displayed next to the items or accessed via mouse actions. Different icon types represent different entity types. Similarly, link attributes determine the link representation (line strength, line color, arrowhead, etc.).
Standard graphs include spoke and wheel, peacock, group, hierarchy and mesh. An analytic component of the visualization is the automatic positioning of the nodes on the screen, i.e., the projection of the graph onto a plane. Different algorithms position the nodes based on the strength of the links between nodes or to agglomerate the nodes into groups of the same kind. Once displayed, the user typically has the ability to move nodes, modify node and link attributes, zoom in, collapse, highlight, hide or delete portions of the graph.
Variable Creation
Link analysis can append new fields to existing records or create entirely new data sets for subsequent modeling stages in a decision system. For example, a new variable for a customer might be the total number of email addresses and credit card numbers linked to that customer.
Search
Link analysis query mechanisms include retrieving nodes and links matching specified criteria, such as node and link attributes, as well as search by example to find more nodes that are similar to the specified example node.
A more complex task is similarity search, also called clustering. Here, the objective is to find groups of similar nodes. These may actually be multiple instances of the same physical entity, such as a single individual using multiple accounts in a similar fashion.
Network Analysis
Network analysis is the search for parts of the linkage graph that play particular roles. It is used to build more robust communication networks and to combat organized crime. This exploration revolves around questions such as:
- Which nodes are key or central to the network?
- Which links can be severed or strengthened to most effectively impede or enhance the operation of the network?
- Can the existence of undetected links or nodes be inferred from the known data?
- Are there similarities in the structure of subparts of the network that can indicate an underlying relationship (e.g., modus operandi)?
- What are the relevant sub-networks within a much larger network?
- What data model and level of aggregation best reveal certain types of links and sub-networks?
- What types of structured groups of entities occur in the data set?
Applications
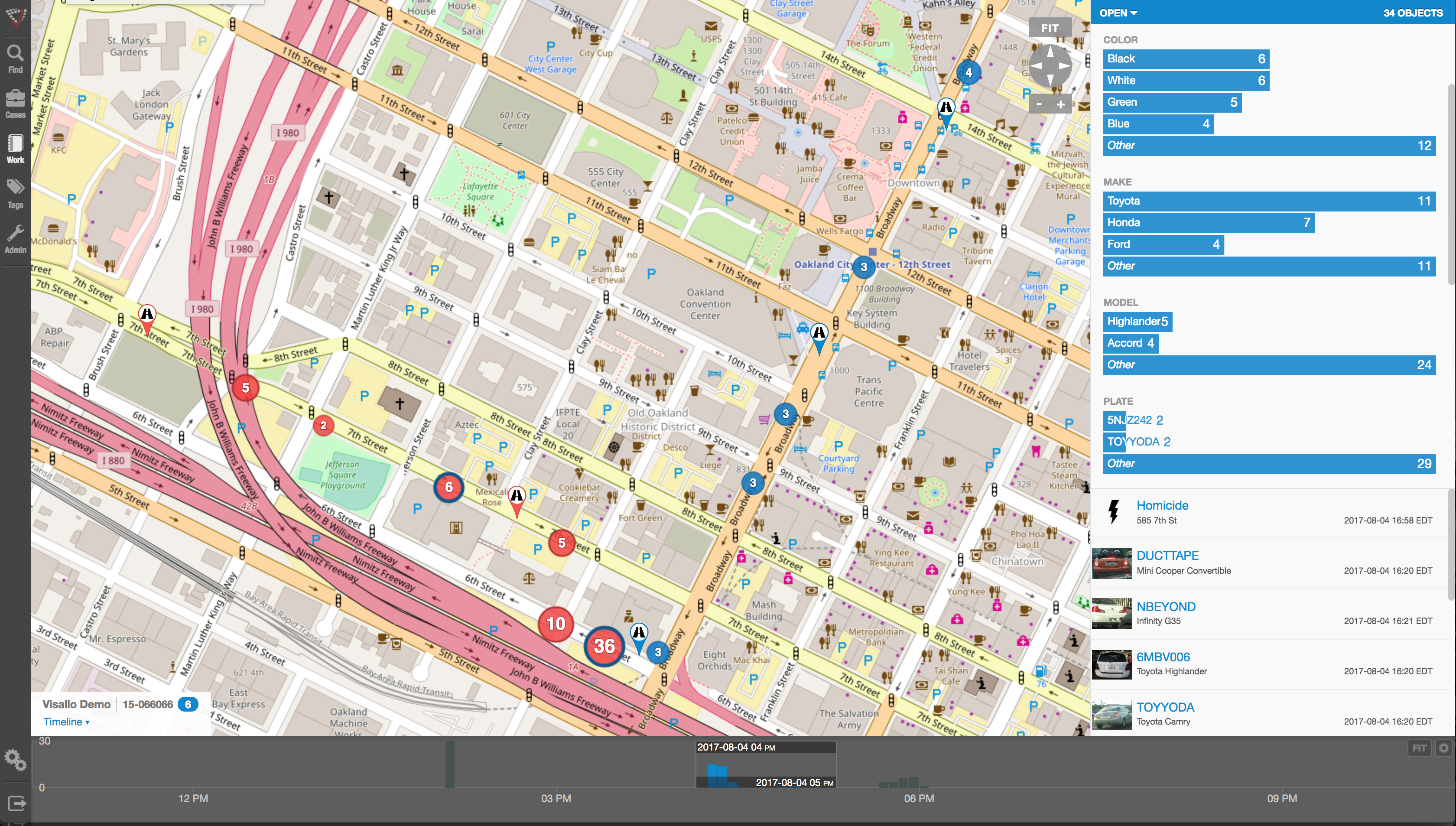
Link analysis tools such as those provided by Crime Tech Solutions are increasingly used in law enforcement investigations, detecting terrorist threats, fraud detection, detecting money laundering, telecommunications network analysis, classifying web pages, analyzing transportation routes, pharmaceuticals research, epidemiology, detecting nuclear proliferation and a host of other specialized applications. For example, in the case of money laundering, the entities might include people, bank accounts and businesses, and the transactions might include wire transfers, checks and cash deposits. Exploring relationships among these different objects helps expose networks of activity, both legal and illegal.
Biometrics and Authentication – A new world of possibilities
This article was written  by Sacha Breite, head of future payments at SIX Payment Services. It originally appeared here on July 20, 2015.
by Sacha Breite, head of future payments at SIX Payment Services. It originally appeared here on July 20, 2015.
The search for a common, international standard of payment authentication is in full flow.
Governments, retailers, banks and (not least) consumers are all eager to find a means of confirming someone’s identity beyond any doubt, secure from external hacking and technologically reliable.
The situation has become more urgent with the wildfire spread of mobile technology, opening up countless opportunities for remote transactions, but placing a growing burden on payment systems to prevent fraud and theft, both of assets and identities.
So, what are the best ways forward?
Here are some of the key technologies, with an analysis of their pros and cons:
Fingerprints and vein recognition
Already in common use at border controls and in many smartphones, fingerprint identification has become widely accepted. But concerns over its reliability and security has dissuaded banks from adopting it for payment authentication.
Some consumers fear that their fingerprint hashdata could be copied and used fraudulently, so they have switched back to pin ID. Younger consumers are more relaxed with the technology and ApplePay can be activated using fingerprint ID.
As technology develops and sensors are more widespread, some are concerned that their fingerprint ID could be captured simply by touching something, without realizing. The technology is likely to remain popular, but probably in combination with other forms of ID.
Facial recognition
Another border control technology which is likely to spread into the commercial world, this once again raises reliability concerns. What happens if one’s face alters its appearance? Can someone be impersonated by showing an image of their face?
A number of extra aspects can tighten security: infrared scanners can tell the difference between a live person and an image; a 3D scan of someone’s head provides further authentication; and iris recognition is becoming more sophisticated.
The new ‘Hello’ function on Windows 10 includes a means of unlocking one’s computer simply by looking at it. So the prospect of going to an ATM, looking at it and then getting cash out, may be possible in future (though some people will object to being filmed, on privacy grounds).
Customers taking ‘selfies’ and using these as authentication, either as a still image or a video, is another emerging form of authentication. Recently MasterCard announced plans to pilot this solution and replace passwords in 3-D Secure protected payments.
Heartbeats
Like our fingerprints and irises, everyone has a unique heartbeat. Using this for identification has the advantage that is it dynamic rather than static and therefore harder to replicate and proves that you are an actual human being.
The technology is part of many current and emerging devices, particularly for sports and fitness use, providing a ready means of integration with other systems, such as transactions or establishing ID.
Wearable technology, whether for health, fashion or communication, will give this type of authentication further impetus. So we can expect to see more of it in the years to come.
Beyond the technologies employed, there are further debates over whose responsibility it should be to develop any common standard. Governments are an obvious place to start, and indeed they have collaborated successfully to introduce border controls using biometric ID.
Yet transactions involving large amounts of money, especially ones using mobile devices, require greater security than this. People are physically present at border points and have to show their passports, so the biometrics are simply an additional security layer.
Most of the initiatives rolled out by governments using biometric ID authentication for health insurance (for example) have failed to work in the commercial sphere.
Card Schemes such as Visa and MasterCard would love to introduce such a system and have it commonly adopted internationally, since it would increase brand loyalty and probably win them new customers.
But so far, the lack of clarity over what kind of technology will be most widely accepted, by governments, consumers and by the legal world, has prevented any major financial service provider taking a leap of faith. Reliability, security and privacy issues remain unresolved.
In some ways, technology is leaping ahead of the best efforts of governments and banks, through applications like Google Street View and Google Image, where individuals can be identified through pictures taken of them without necessarily having their consent. And commercial services such as Amazon, PayPal and eBay have pioneered slimmed-down ID procedures, which may become more widely adopted.
An ever increasing amount of data is being stored on all of us, which will enable identification through many differing avenues. Irrespectively of the current position of biometrics and technology, it is vital for banking and payment infrastructure providers like SIX Payment Services, to provide high levels of security and reliability. In the near future we can expect further innovations to appear in this space, however it is still unclear which will form the basis of a single global standard, until the dust has settled from the current burst of activity.
The Name Game Fraud
 Posted by Douglas Wood, Editor. Alright everybody, let’s play a game. The name game!
Posted by Douglas Wood, Editor. Alright everybody, let’s play a game. The name game!
“Shirley, Shirley bo Birley. Bonana fanna fo Firley. Fee fy mo Mirley. Shirley!” No, not THAT name game. (Admit it… you used to love singing the “Chuck” version, though.)
The name game I’m referring to is slightly more sinister, and relates to the criminal intent to deceive others for gain by slightly misrepresenting attributes in order to circumvent fraud detection techniques. Pretty much anywhere money, goods, or services are dispensed, folks play the name game.
Utilities, Insurance, Medicaid, retail, FEMA. You name it.
Several years ago, I helped a large online insurance provider determine the extent to which they were offering insurance policies to corporations and individuals with whom they specifically did not want to do business. Here’s what the insurer knew:
- They had standard application questions designed to both determine the insurance quote AND to ensure that they were not doing business with undesirables. These questions included things such as full name, address, telephone number, date of birth, etc… but also questions related to the insured property. “Do you live within a mile of a fire station?”, Does your home have smoke detectors?”, and “Is your house made of matchsticks?”
- On top of the questions, the insurer had a list of entities with whom the knew they did not want to do business for one reason or another. Perhaps Charlie Cheat had some previously questionable claims… he would have been on their list.
In order to circumvent the fraud prevention techniques, of course, the unscrupulous types figured out how to mislead the insurer just enough so that the policy was approved. Once approved, the car would immediately be stolen. The house would immediately burn down, etc.
The most common way by which the fraudsters misled the insurers was a combination of The Name Game and modifying answers until the screening system was fooled. Through a combination of investigative case management and link analysis software, I went back and looked at several months of historical data and found some amazing techniques used by the criminals. Specifically, I found one customer who made 19 separate online applications – each time changing just one attribute or answer slightly – until the policy was issued. Within a week of the policy issue, a claim was made. You can use your imagination to determine if it was a legitimate claim. 😀
This customer, Charlie Cheat (obviously not his real name), first used his real name, address, telephone number, and date of birth… and answered all of the screening questions honestly. Because he did not meet the criteria AND appeared on an internal watch list for having suspicious previous claims, his application was automatically denied. Then he had his wife, Cheri Cheat, complete the application in hopes that the system would see a different name and approve the policy. Thirdly, he modified his name to Charlie Cheat, Chuck E. Cheat, and so on. Still no go. His address went from 123 Fifth Street to 123-A 5th Street. You get the picture.
Then he began to modify answers to the screening questions. All of a sudden, he DID live within a mile of a fire station… and his house was NOT made of matchsticks… and was NOT located next door to a fireworks factory. After almost two dozen attempts, he was finally issued the policy under a slightly revised name, a tweak in his address, and some less-than-truthful answers on the screening page. By investing in powerful investigative case management software with link analysis and fuzzy matching this insurer was able to dramatically decrease the number of policies issued to known fraudsters or otherwise ineligible entities.
Every time a new policy is applied for, the system analyzes the data against previous responses and internal watch lists in real time. In other words, Charlie and Cheri just found it a lot more difficult to rip this insurer off. These same situations occur in other arenas, costing us millions annually in increased taxes and prices. So, what happened to the Cheats after singing the name game?
Let’s just say that after receiving a letter from the insurer, Charlie and Cheri started singing a different tune altogether.
Using Link Analysis to untangle fraud webs
Posted by Douglas Wood, Editor.
NOTE: This article originally appeared HERE by Jane Antonio. I think it’s a great read…
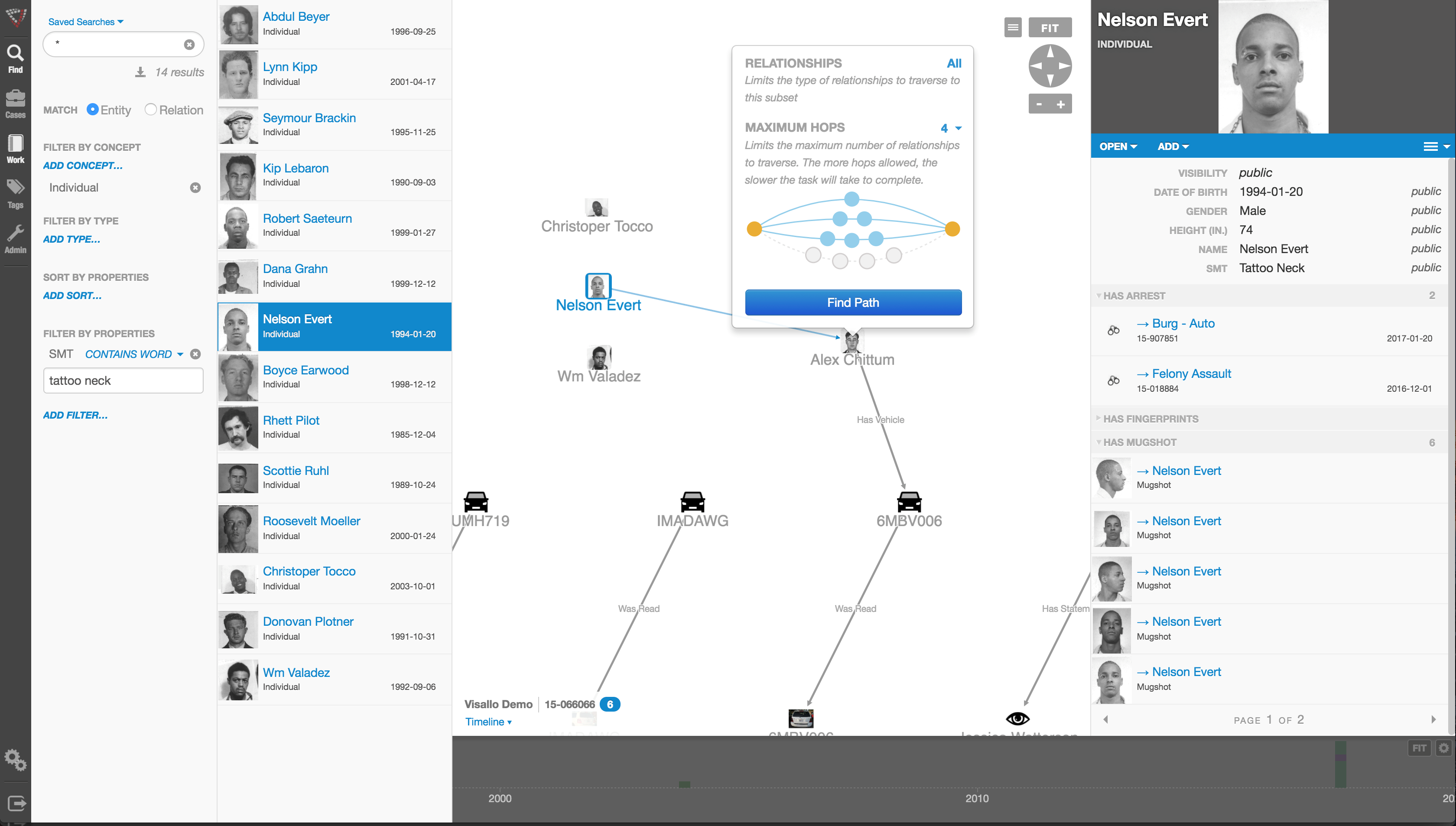
Link analysis has become an important technique for discovering hidden relationships involved in healthcare fraud. An excellent online source, FierceHealthPayer:AntiFraud, recently spoke to Vincent Boyd Bryant about the value of this tool for payer special investigations units.
A former biometric scientist for the U.S. Department of Defense, Bryant has 30 years of experience in law enforcement and intelligence analysis. He’s an internationally-experienced investigations and forensics expert who’s worked for a leading health insurer on government business fraud and abuse cases.
How does interactive link analysis help insurers prevent healthcare fraud? Can you share an example of how the tool works?
One thing criminals do best is hide pots of money in different places. As a small criminal operation becomes successful, it will often expand its revenue streams through associated businesses. Link analysis is about trying to figure out where all those different baskets of revenue may be. Insurers are drowning in a sea of theft. Here’s where link analysis becomes beneficial. Once insurers discover a small basket of money lost to a criminal enterprise, then serious research needs to go into finding out who owns the company, who they’re associated with, what kinds of business they’re doing and if there are claims associated with it.
You may find a clinic, for example, connected to and working near a pharmacy, a medical equipment supplier, a home healthcare services provider and a construction company. Diving into those companies and what they do, you find that they’re serving older patients for whom multiple claims from many providers exist. The construction company may be building wheelchair ramps on homes. And you may find that the providers are claiming payment for dead people. Overall, using this tool requires significant curiosity and a willingness to look beyond the obvious.
Any investigation consists of aggregating facts, generating impressions and creating a theory about what happened. Then you work to confirm or disconfirm your theory. It’s important to have tools that let you take large masses of facts and visualize them in ways that cue you to look closer.
Let’s say you investigate a large medical practice and interview “Doctor Jones.” The day after the interview, you learn through link analysis that he transferred $11 million from his primary bank account to the Cayman Islands. And in looking at Dr. Jones’ phone records, you see he called six people, each of whom was the head of another individual practice on whose board Dr. Jones sits. Now the investigation expands, since the timing of those phone calls was contemporaneous to the money taking flight.
Why are tight clusters of similar entities possible indicators of fraud, waste or abuse?
Bryant: When you find a business engaged in dishonest practices and see its different relationships with providers working out of the same building, this gives rise to reasonable suspicion. The case merits a closer look. Examining claims and talking to members served by those companies will give you an indication of how legitimate the operation is.
What are the advantages of link analysis to payer special investigation units, and how are SIUs using its results?
Bryant: Link analysis can define relationships through data insurers haven’t always had, data that traditionally belonged to law enforcement.
Link analysis results in a visual reference that can take many forms: It can look like a family tree, an organizational chart or a time line. This reference helps investigators assess large masses of data for clustering and helps them arrive at a conclusion more rapidly.
Using link analysis, an investigator can dump in large amounts of data–such as patient lists from multiple practices–and see who’s serving the same patient. This can identify those who doctor shop for pain medication, for example. Link analysis can chart where this person was and when, showing the total amount of medication prescribed and giving you an idea of how the person is operating.
What types of data does link analysis integrate?
Bryant: Any type of data that can be sorted and tied together can be loaded into the tool. Examples include telephone records, addresses, vehicle information, corporate records that list individuals serving on boards and banking and financial information. Larger supporting documents can be loaded and linked to the charts, making cases easier to present to a jury.
Linked analysis can pull in data from state government agencies, county tax records or police records from state departments of correction and make those available in one bucket. In most cases, this is more efficient than the hours of labor needed to dig up these types of public records through site visits.
Is there anything else payers should know about link analysis that wasn’t covered in the above questions?
Bryant: The critical thing is remembering that you don’t know what you don’t know. If a provider or member is stealing from the plan in what looks like dribs and drabs, insurers may never discover the true extent of the losses. But if–as a part of any fraud allegation that arises–you look at what and who is associated with the subject of the complaint, what started as a $100,000 questionable claims allegation can expose millions of dollars in inappropriate billings spread across different entities.
Perhaps a nice change at NICE Actimize?
Posted by Douglas Wood, Editor. http://www.linkedin.com/in/dougwood
Though not publicly released, news out of NICE Actimize is that long-time CEO Amir Orad is leaving the company effective May 1. Indicative of the ‘what a small world this is’ nature of the financial crimes technology marketplace, former Pegasystems co-founder and head of Americas for BAE Systems Detica, Joe Friscia, will be taking over the helm at that time.
Mr. Orad led NICE Actimize’s product and strategy functions prior to his five year tenure as CEO. During his tenure, he scaled the business size over six-fold. He is also a founding board member at BillGuard the venture backed personal finance analytics and security mobile app company.
Prior to Actimize, Orad was co-founder and CMO of Cyota a cyber security and payment fraud cloud company protecting over 100 million online users, acquired by RSA Security for $145M. Following the acquisition, he was VP Marketing at RSA.
I’ve known both Amir and Joe for several years, and have a tremendous amount of respect for both gentlemen. While it’s sad to see Amir leave the organization, I know that his rather large shoes will be more than adequately filled by Mr. Friscia.
Joe’s background is well-suited to this new position, and all of us here at FightFinancialCrimes wish him well. Joe joined Detica when BAE Systems acquired Norkom Technologies in early 2011, where he served as General Manager and Executive Vice President of the Americas. Joe led the rapid growth of Norkom in the Americas, with direct responsibility for sales, revenue and profit as well as managing multi-discipline teams based in North America. Prior to Norkom, Joe helped start Pegasystems Inc in 1984, a successful Business Process Management software company that went public in 1996.
Best of luck to Amir in his new ventures, and to Joe as he guides Actimize into it’s next phase.
Part Two: Major Investigation Analytics – Big Data and Smart Data
Posted by Douglas Wood, Editor.
As regular readers of this blog know, I spend a great deal of time writing about the use of technology in the fight against crime – financial and otherwise. In Part One of this series, I overviewed the concept of Major Investigation Analytics and Investigative Case Management.
I also overviewed the major providers of this software technology – Palantir Technologies, Case Closed Software, and Visallo. The latter two recently became strategic partners, in fact.
The major case for major case management (pun intended) was driven home at a recent crime and investigation conference in New York. Full Disclosure: I attended the conference for educational purposes as part of my role at Crime Tech Weekly. Throughout the three day conference, speaker after speaker talked about making sense of data. I think if I’d have heard the term ‘big data’ one more time I’d have gone insane. Nevertheless, that was the topic du jour as you can imagine, and the 3 V’s of big data – volume, variety, and velocity – remain a front and center topic for the vendor community serving the investigation market.
According to one report, 96% of everything we do in life – personal or at work – generates data. That statement probably best sums up how big ‘big data’ is. Unfortunately, there was very little discussion about how big data can help investigate major crimes. There was a lot of talk about analytics, for sure, but there was a noticeable lack of ‘meat on the bone’ when it came to major investigation analytics.
Nobody has ever yelled out “Help, I’ve been attacked. Someone call the big data!”. That’s because big data doesn’t, in and by itself, do anything. Once you can move ‘big data’ into ‘smart data’, however, you have an opportunity to investigate and adjudicate crime. To me, smart data (in the context of investigations) is a subset of an investigator’s ability to:
- Quickly triage a threat (or case) using only those bits of data that are most immediately relevant
- Understand the larger scope of the crime through experience and crime analytics, and
- Manage that case through intelligence-led analytics and investigative case management, data sharing, link exploration, text analytics, and so on.
Connecting the dots, as they say. From an investigation perspective, however, connecting dots can be daunting. In the children’s game, there is a defined starting point and a set of rules. We simply need to follow the instructions and the puzzle is solved. Not so in the world of the investigator. The ‘dots’ are not as easy to find. It can be like looking for a needle in a haystack, but the needle is actually broken into pieces and spread across ten haystacks.
Big data brings those haystacks together, but only smart data finds the needles… and therein lies the true value of major investigation analytics.
Part 2: Investigating the Investigations – X Marks the Spot
Posted by Douglas Wood, Editor. http://www.linkedin.com/in/dougwood
Part One of this series is HERE.
Most of the financial crimes investigators I know live in a world where they dream of moving things from their Inbox to their Outbox. Oh, like everyone else, they also dream about winning the lottery, flying without wings, and being naked in public. But in terms of the important roles they perform within both public and private sectors, there is simply Investigating (Inbox) and Adjudication (Outbox). Getting there requires a unique blend of their own capabilities, the availability of data, and the technology that allows them to operate. In the diagram below, ‘X‘ marks the spot where crimes are moved from the Inbox to the Outbox. Without any of those three components, an investigation becomes exponentially more difficult to conclude.
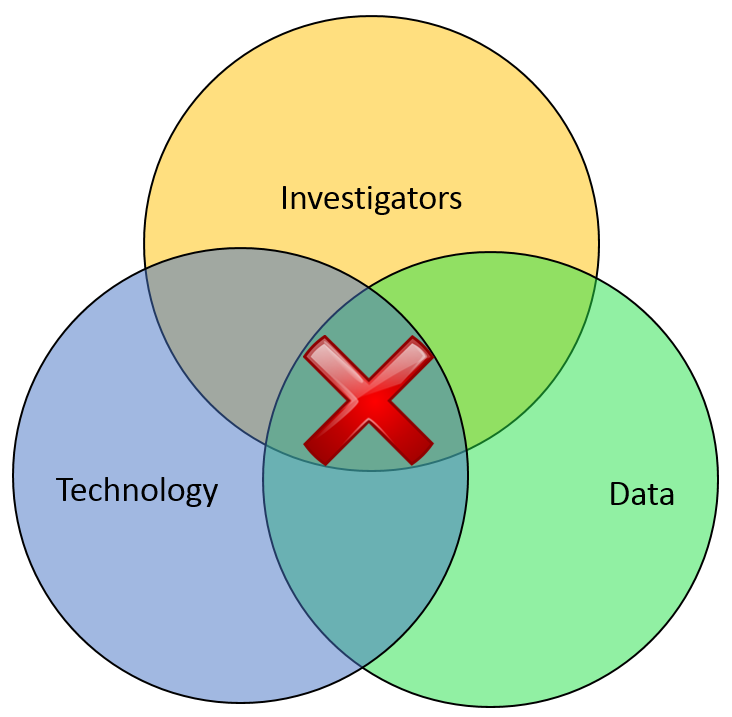
In part one of this article two weeks ago, I wrote about the Investigation Management & Adjudication (IMA) side of financial crimes investigations. I coined that term to call out what is arguably the most integral component of any enterprise fraud management (EFM) ecosystem. The original EFM overview is here.
“The job is almost unrecognizable to those who once used rotary phones in smoke filled offices…
Twenty years ago, IMA was based primarily upon human eyes. Yes, there were technology tools available such as Wordperfect charts and Lotus 1-2-3 spreadsheets, but ultimately it was the investigator who was tasked with finding interesting connections across an array of data elements including handwritten briefs, telephone bills, lists of suspect information, and discussions with other investigators. The job got done, though. Things moved from the Inbox to the Outbox, arrests were made and prosecutions were successful. Kudos, therefore, to all of the investigators who worked in this environment.
Fast forward to today, and the investigator’s world is dramatically different. The job is the same, of course, but the tools and mass availability of data has made the job almost unrecognizable to those who once used rotary phones in smoke filled offices. Organizations began building enterprise data warehouses designed to provide a single version of the truth. Identity Resolution technology was implemented to help investigators recognize similarities between entities in that data warehouse. And today, powerful new IMA tools are allowing easy ingestion of that data, improved methods for securely sharing across jurisdictions, automated link discovery, non-obvious relationship detection, and interactive visualization tools, and -importantly – packaged e-briefs which can be understood and used by law enforcement, prosecutors, or adjudication experts.
“Without any of these components, everything risks falling to the outhouse…
With all these new technologies, surely the job of the Investigator is becoming easier? Not so fast.
IMA tools – and other EFM tools – do nothing by themselves. The data – big data – does nothing by itself. It just sits there. The best investigators – without tools or data – are rendered impotent. Only the combination of skilled, trained investigators using the best IMA tools to analyze the most useful data available results in moving things from the Inbox to the Outbox. Without any of these components… everything eventually risks falling to the Outhouse.
Kudos again, Mr. and Mrs. Investigator. You’ll always be at the heart of every investigation. Here’s hoping you solve for X every day.
To 314(b) or not to 314(b)?
Posted by Douglas Wood, Editor. http://www.linkedin.com/in/dougwood
FinCEN today (November 1, 2013) released a fact sheet regarding data sharing between financial institutions under the Section 314(b) of the US Patriot Act.
314(b) provides financial institutions with the ability to share information with one another, under a safe harbor that offers protections from liability, in order to better identify and report potential money laundering or terrorist activities. 314(b) information sharing is a voluntary program, and FinCEN has always encouraged its use.
A few years ago, I spent considerable time looking at the overall 314(b) program. I interviewed dozens of Chief Compliance Officers (CCO) and AML/Fraud experts. I found that, despite the benefits to financial institutions – reduction of fraud loss, more complete SARs filings, shedding light on financial trails, etc – the program was not particularly well-utilized. The system, for all it’s good intentions, is very manual.
Imagine you are a 314(b) officer at a financial institution. Your job is to facilitate the data sharing amongst the community. So, much of your time is spent interacting with your CCO on which specific cases should be shared, and with whom. When you get that information, you open up you financial crimes investigation tools, and begin contacting your counterparts across the U.S. and asking them “Hey, do you know anything about Douglas Wood?” You’re calling the other officers completely blind with no idea whatsoever if they know Doug. In the meantime, your voicemail inbox is being flooded with other calls from other institutions asking if you know a bunch of other people (or entities).
Finding the institutions that know Douglas Wood is a lot like looking for a needle in a haystack… except you don’t know which haystacks to look in. The system too often grinds to a halt, despite some excellent work being done by 314(b) officers across the country. There has to be a better way, and some have proposed a data contribution system where financial institutions upload their bad guy data into one large third-party haystack, making the needle a little easier to find. As an advocate for the use of technology in the fight against financial crimes, I hope that model finds some success. The problem, of course, is that banks are LOATHED to put their data in the hands of a third party. Also, it’s typically up to each individual bank to decide if and when they choose to upload their data to be inter-mingled with other institutions. Far too often, it is not entirely reliable and not particularly current.
There is a better way. Several years ago, working with some tech-savvy employees, I envisioned a member-based 314(b) program where each institution maintained total control of their data. The model does not require individual banks to contribute their data for inter-mingling. All ‘bad guy’ data sits and remains securely behind the banks’ respective firewalls. When an individual bank sends out a request to find out who, if anyone, may have information about a suspicious entity, the request is systematically sent out to all members using a secure network such as SWIFT, for example. That electronic search returns to the querying bank only a risk score which indicates the likelihood that another member is investigating the same entity.
No personally identifiable information (PII) is ever shared, yet the search is productive. The enquiring bank now knows that the person of interest was found in the bad guy data from other participating institutions. With this information in hand, the respective 314(b) officers can move their voicemail exchanges from “Have you ever heard of Douglas Wood” to “We’re both investigating Douglas Wood… let’s do it together.” The time-consuming, manual efforts are dramatically reduced and more bad guys are put away.
So if the question is to 314(b) or not to 314(b), perhaps the answer lies in data privacy compliant technology.