 Crime Tech Solutions, LLC – a fast growing, vibrant software company based in Leander, TX today announced that a large, coastal city in California has selected them to provide sophisticated link and social network analysis software.
Crime Tech Solutions, LLC – a fast growing, vibrant software company based in Leander, TX today announced that a large, coastal city in California has selected them to provide sophisticated link and social network analysis software.
Crime Tech Solutions was awarded the contract based upon its price/performance leadership in the world of big data analytics for law enforcement and other investigative agencies.
Link analysis software is used by investigators to visualize hidden connections between people, places, and things within large and disparate data sets.
“Our link analysis software gives investigators an edge in the way they analyze data”, said Crime Tech Solutions’ CEO, Doug Wood. “By finding and displaying those hard to find connections and anomalies that reside in different data stores, our software helps investigative agencies more clearly see how networks of entities exist.”
Crime Tech Solutions said that the software implementation is already underway, and that the software will make life a little more miserable for criminals in the Southern California city.
The company also develops investigative case management and criminal intelligence software for law enforcement agencies of all sizes.
Tag Archives: social network analysis
Hunting for D.B. Cooper – A study in analytics.
The following article originally appeared at In Public Safety, and is a highly recommended read. It was written by Erik Kleinsmith at American Military University.
Crime Tech Weekly is posting the article in its entirety for our readers’ convenience…
By Erik Kleinsmith
Staff, Intelligence Studies, American Military University
On November 24, 1971, a man using the name Dan Cooper purchased a $35 one-way airline ticket from Portland, Oregon, to Seattle, Washington. Not long after takeoff, he hijacked Northwest Orient Flight 305 and demanded $200,000 in cash along with two parachutes, which he received upon landing in Seattle. He then ordered the plane to take off and fly to Mexico City; during that flight, he jumped from the aircraft into the Oregon wilderness, securing his place as the only unsolved case in FAA history.

In early 2011, following a host of other investigations — both private and government-led — Tom Colbert picked up the trail of the man now known as D.B. Cooper. As an investigative reporter and producer living in Southern California, Colbert was tipped off by a source in the illicit drug trade who had credible — albeit circumstantial — evidence that D.B. Cooper was alive and living in California. Over the next few years, Colbert invested incredible amounts of time and personal resources toward tackling a 45-year-old mystery that so many other investigators before him had failed to solve.
A New Approach to Finding D.B. Cooper
Colbert assembled a large group of leading private investigators, detectives, attorneys, profilers and other subject matter experts into a group he called the “Cold Case Team.” He also knew he needed the expertise of intelligence professionals to help him organize and analyze all the evidence related to this case. While intelligence analysts almost always focus on using their skills for predictive analysis predictive analysis (i.e., what’s going to happen), Colbert knew having people proficient in intelligence collection and analysis would provide unique insight into a case that was decades old.
In December 2011, Colbert elicited my help while I was involved in an Army intelligence training contract. We had been associates and friends for a few years and he knew about my involvement in the Able Danger program. As a student, practitioner, developer and instructor of intelligence methodology, I was interested in his investigation because it was another chance for me to adapt intelligence analytical methods to a cold (very cold) case. I immediately agreed to support his efforts; he sent me a copy of a dossier on the man he suspected was D.B. Cooper.
It contained photos, maps, interview summaries and many other pieces of evidence connecting this man to the D.B. Cooper incident. Much of the initial information was secondhand and circumstantial, so Colbert was using it to provide further investigative leads for the Cold Case Team members.
Here is where I make my quick disclaimer: Collecting information on U.S. persons for intelligence purposes is prohibited by several federal regulations with very few specific exceptions. Even though I would be supporting a private investigation, I was working as a defense contractor at the time and therefore felt it was important to follow the spirit of these restrictions by creating products based only upon what the Cold Case Team provided. Neither myself nor my colleague independently searched for or collected any additional information for any part of this investigation.
That being said, it was an exceptional opportunity to use analytical intelligence techniques to assist in this investigation.
Using Link Analysis Techniques in the Investigation
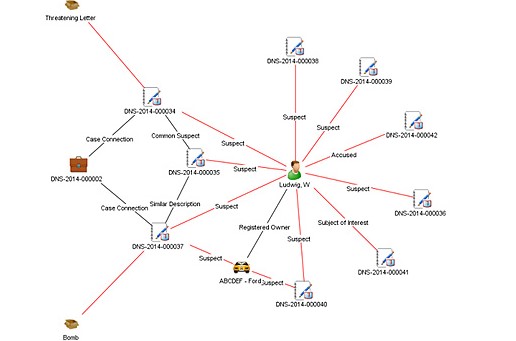
In his meetings with various law enforcement officials, Colbert had grown frustrated that no one was taking the time to look through the dossier and consider the evidence. I gave it to one of my senior instructors, David D’Alessio, and asked him to make a link chart of associations using one of the best link analysis software programs available to us. A link chart is a graphic representation of the people, events, and significant items of interest (such as a bank account or address) associated with a particular subject. The key to these charts are the associations or “links” between each of the people, events and items in it.

Creating this chart was a painstaking process because D’Alessio had to go through each paragraph line by line, identify the relative linkages between entities and enter them into the software program. The initial link chart started with the main suspect and then drew graphic linkages to all his known associates their connections to third parties, and a host of other associations to events, locations, aliases and specific pieces of physical evidence. Working with D’Alessio and Colbert over several iterations of this chart, we ended up with a 3×2 foot poster that, to the untrained eye, looked a lot like charts shown in court or on television shows like Law and Order. There were hundreds of links to the main suspect, the many aliases he used over the years to include military records and associations that placed him in the vicinity of the Portland, Oregon area during the time of the hijacking.
The benefit of link analysis charts is that they do more than just show connections between entities. A link chart tells a comprehensive visual story and conveys a dynamic and detailed summary of information from the document supporting it. This technique proved immensely successful, as the visual representation helped capture attention and interest from outside parties.
How Intelligence Analysis Aided in the Investigation
Besides taking text-based information and turning it into a graphic visualization for presentation purposes, a link chart also helped the investigation in other ways. First, Colbert and his team were able to see gaps in the information where investigators needed to dig deeper. He could also see which links were strong and which were weak or tenuous. The team could then plan their investigations more effectively by identifying which gaps needed to be filled and prioritize how to best use their limited resources.
This chart also had a psychological value to the Cold Case Team. In 2013, one of the team’s private investigators presented it directly to the suspect and asked him to come forward. The hope was that once the suspect knew there was a vast amount of information on the identity of D.B. Cooper (not to mention it featured his picture right at the center). Revealing this chart helped Colbert enter into negotiations with the suspect’s lawyer and he came very close to a deal that would potentially involve an admission. Unfortunately, Colbert and the Cold Case Team were turned down at the last minute due to what we believe was his fear of being connected to other illicit activities.
Why Law Enforcement Must Partner More Often with Intelligence Agencies
 Ultimately, this case demonstrates that intelligence analysis can play a crucial part in law enforcement investigations, both as a predictive asset as well as an investigative one. The D.B. Cooper investigation is decades old, but there are many other cases that are not. Other law enforcement agencies can use the techniques tested in this case to assist with other unsolved crimes, missing persons and patterns of criminal activity. It’s important for law enforcement authorities to remember that analysts in the intelligence field bring with them a toolkit that provides both unique and specialized analytical methods that can offer new perspectives. Bringing intelligence analysts into the fold of law enforcement can enhance a crime-solving team.
Ultimately, this case demonstrates that intelligence analysis can play a crucial part in law enforcement investigations, both as a predictive asset as well as an investigative one. The D.B. Cooper investigation is decades old, but there are many other cases that are not. Other law enforcement agencies can use the techniques tested in this case to assist with other unsolved crimes, missing persons and patterns of criminal activity. It’s important for law enforcement authorities to remember that analysts in the intelligence field bring with them a toolkit that provides both unique and specialized analytical methods that can offer new perspectives. Bringing intelligence analysts into the fold of law enforcement can enhance a crime-solving team.
The federal government has awesome capabilities in intelligence collection and investigation but they are not alone. There is an equally awesome, yet untapped capability, in the commercial sector and among academia to support investigations like this and other more current cases. There are uncounted numbers of undergraduate and graduate students in criminal justice, data analysis and intelligence studies courses who would be eager to support a future case. In addition, there are also many retired law enforcement and intelligence professionals who would be eager to lend their experience and subject matter expertise to similar cases and problem sets, if only to satisfy the investigative bug still within them.
While the FBI officially closed its investigation in the D.B. Cooper case earlier this year, it has not been closed in the eyes of the Cold Case Team. This team continues to move forward with its own investigation, relying on intelligence analysis methods to support them and continue to evaluate every bit of evidence in new ways.

Crime Tech Solutions Acquires Case Closed Software
June 1, 2016 (Austin, TX) Crime Tech Solutions, LLC, a leading provider of analytics and investigation software for law enforcement and commercial markets, today announced that it has acquired Cleveland, TN based Case Closed Software in a cash transaction. The terms of the deal were not released, but according to Crime Tech Solutions’ founder and president Douglas Wood, the acquisition brings together two dynamic and fast-growing software companies with an unparalleled complement of technologies.
“For Crime Tech Solutions, the opportunity to add Case Closed Software into the fold was too good to pass up” said Mr. Wood. “We think that the technology offered by Case Closed helps to further differentiate us in the market as the price performance leader for this type of investigative solution.”
Crime Tech Solutions, based in the city of Leander, TX, delivers advanced analytics and investigation software to commercial investigators and law enforcement agencies across the globe. Their solution suite includes criminal intelligence software, sophisticated crime analytics with geospatial mapping, and powerful link analysis and visualization software. The company says that the addition of Case Closed Software expands those offerings even further.
Case Closed Software develops and markets investigative case management software specifically designed for law enforcement agencies. The suite is built around four primary software products including best-in-class investigative case management software, property and evidence tracking, a gang database tool, and an integrated link analysis and data visualization tool. The company also plans to release the solution as Case Closed Cloud for cloud-based access.
“Case Closed couldn’t be happier than to be joining Crime Tech Solutions,” said Keith Weigand, the company’s founder. “The blending of our technologies creates a suite that will add tremendous value to our mutual customers, and will be hard for others to duplicate.”
According to both Mr. Weigand and Mr. Wood, the name Case Closed will continue on as the product brand, given its widespread popularity and loyal customer base. Crime Tech Solutions is expected to retain all Case Closed employees, with Mr. Weigand joining as the company’s chief technical officer.
Crime Tech Solutions says it expects continued growth via ongoing software sales and strategic acquisitions.
About Crime Tech Solutions
(NOTE: Crime Tech Solutions is an Austin, TX based provider of crime and fraud analytics software for commercial and law enforcement groups. Our offerings include sophisticated Case Closed™ investigative case management and major case management, GangBuster™ gang intelligence software, powerful link analysis software, evidence management, mobile applications for law enforcement, comprehensive crime analytics with mapping and predictive policing, and 28 CFR Part 23 compliant criminal intelligence database management systems.)
Link Analysis and Crime – An examination.
Posted by Tyler Wood, Operations Manager at Crime Tech Solutions
 The topic of fraud is widely discussed, and the focus of thousands upon thousands of articles. Television shows such as Crime, Inc and American Greed have become popular due, in part, to our fascination with the topic of fraud.
The topic of fraud is widely discussed, and the focus of thousands upon thousands of articles. Television shows such as Crime, Inc and American Greed have become popular due, in part, to our fascination with the topic of fraud.
The organizations that are affected by fraud are also fascinated… but for entirely different reasons. Some estimates suggest that the US economy loses 11 trillion dollars each year due to one form of fraud or another. It’s little wonder, therefore, that the companies most frequently defrauded have been heavily investing in anti-fraud technologies at an increasing rate over the past decade or more.
The biggest problem with fraud, of course, is that it is always evolving in a very Darwinian fashion. Like a living, breathing entity, fraud schemes change over time in order to survive. As the targets of fraud schemes put new policies, procedures and/or systems to deter the activities, the schemes modify and find new ways to survive.
So, since the nature of criminal activity is such that they constantly change, how do investigators find a fool proof methodology to ensure they are 100% safe from them? The answer, of course, is that they can’t. They never will; at least not until we live in a world such as the one depicted in the 2002 film Minority Report, starring Tom Cruise. In that movie, criminals are arrested prior to committing a crime based upon the predictions of psychics called ‘Precogs’. Corporations and individual targets of fraud can only wish.
Nope, there are no Precogs running around locking up would-be practitioners of fraud that would protect banks, insurance companies, Medicaid and Medicare programs, victims of Ponzi schemes, victims of identity theft, and countless others. Instead, organizations rely upon skilled knowledge workers using purpose-built crime and fraud analytics technology that can detect anomalies in patterns, suspicious transactions, hotspot mapping, networks of fraudsters, and other sophisticated data analytics tools.
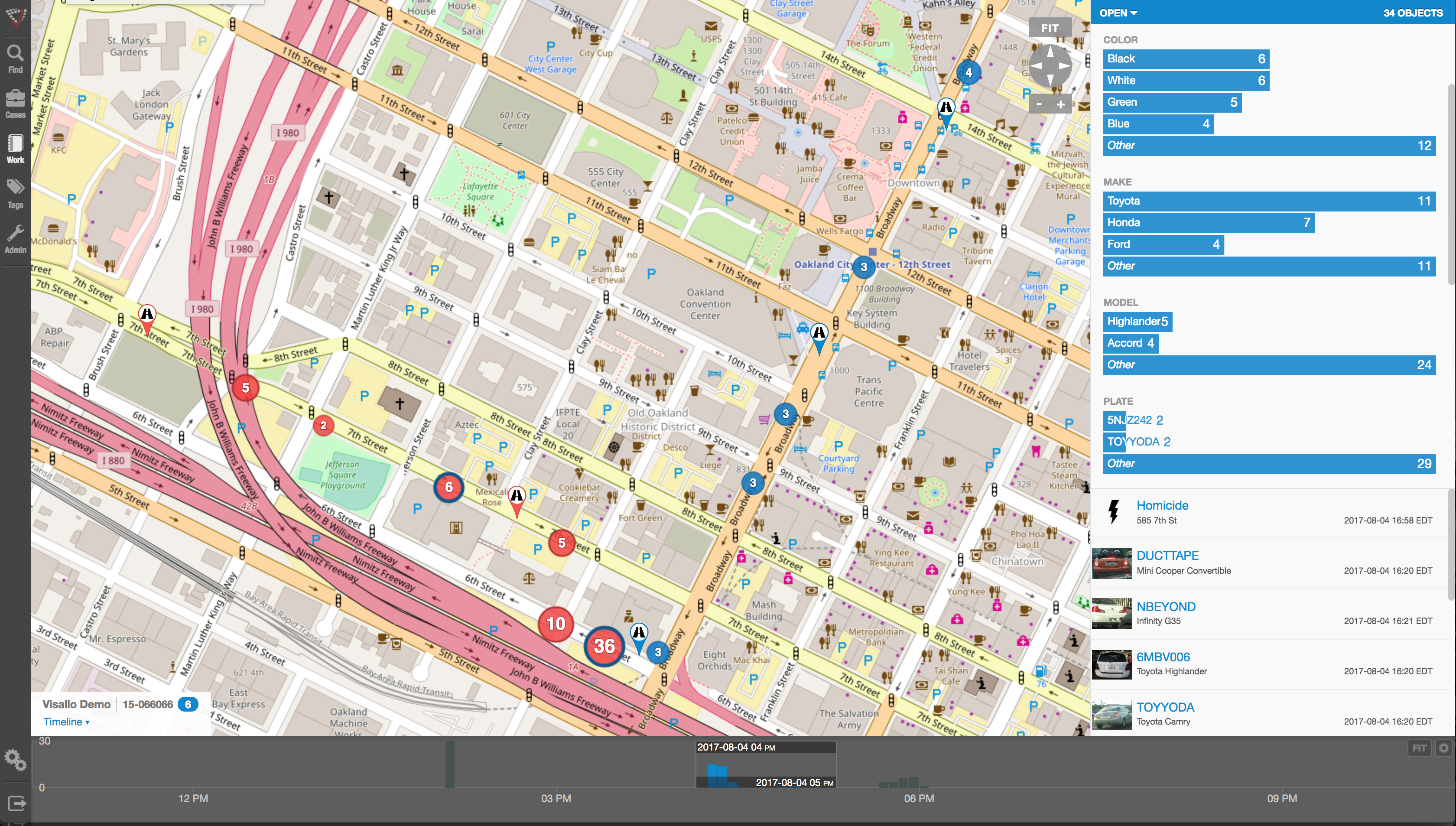
Crime and fraud analytics
Any discussion of analytics and investigation software must touch upon the topic of ‘big data’. No longer just a buzz word, big data literally fuels the insights gathered by organizations in every area of business. Naturally, then, organizations who have been traditionally targeted by fraudsters have increasingly invested in crime technology such as investigation software and analytics in order to exploit the phenomenon.
 Of course, big data in and by itself does nothing. It just sits there. Nobody has ever yelled “Help! We’ve been defrauded! Call the big data!” Big data is only useful when it can be transformed into ‘smart data’. In other words, understanding the big picture of costly fraudulent activities is not akin to understanding the specifics of ‘who’ is defrauding you, and ‘how’ they are doing it.
Of course, big data in and by itself does nothing. It just sits there. Nobody has ever yelled “Help! We’ve been defrauded! Call the big data!” Big data is only useful when it can be transformed into ‘smart data’. In other words, understanding the big picture of costly fraudulent activities is not akin to understanding the specifics of ‘who’ is defrauding you, and ‘how’ they are doing it.
Those questions can best be answered through the powerful data mining and link analysis software tools offered by Austin, TX based Crime Tech Solutions in partnership with Sterling, VA based Visallo. Effective link analysis complements big data analytics platforms, helping to expose previously undetected fraud, and the entities (people or organizations) committing it.
Link Analysis – Transforming big data into smart data
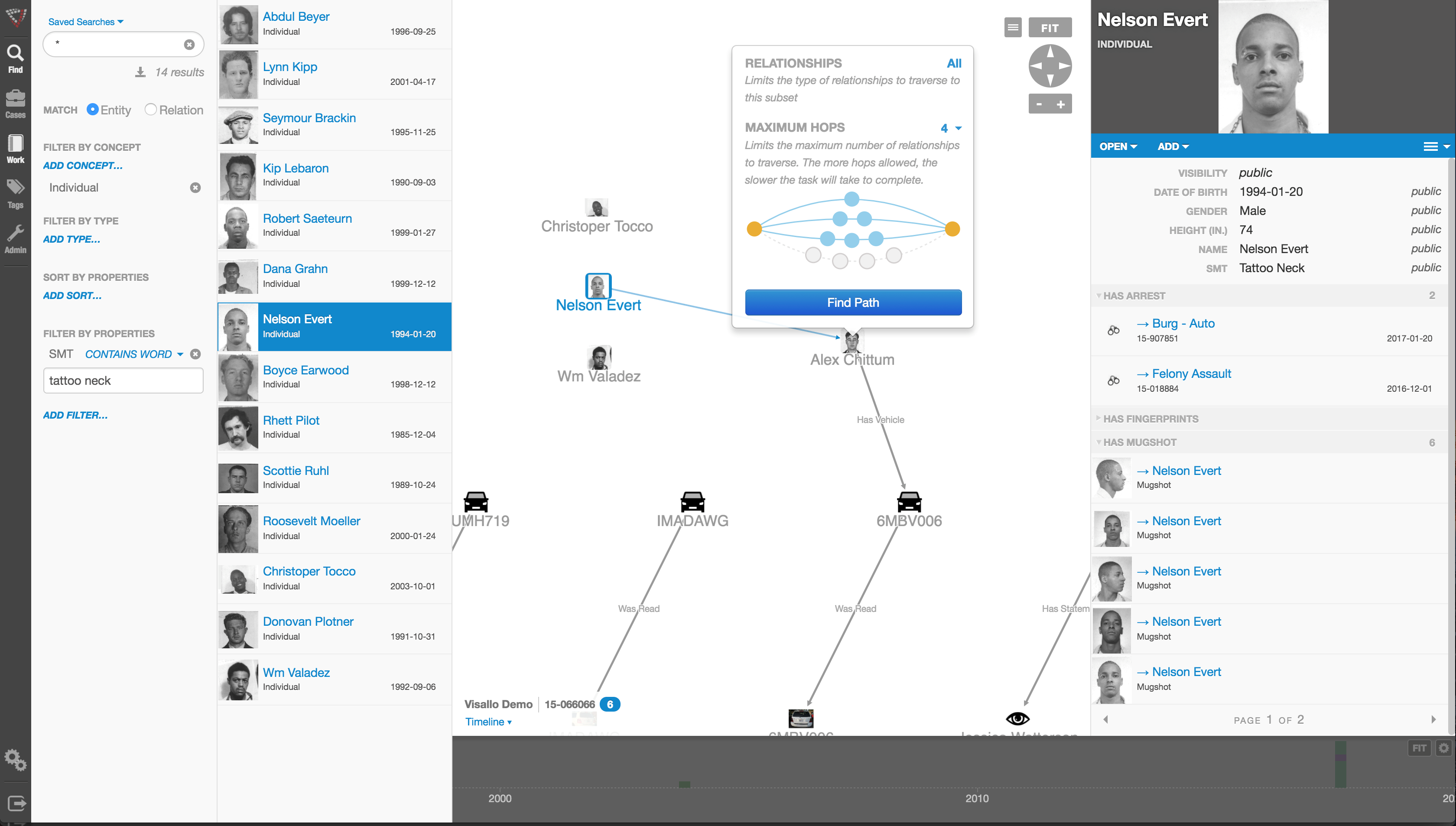
By definition, link analysis is a data analysis technique that examines relationships among people, places, and things. As a visual tool, link analysis provides users a powerful method to quickly understand and ‘see’ what is happening. Because of this, it is widely used by financial institutions such as banks and insurance companies to uncover criminal networks, improve fraud investigations, detect insider fraud, and expose money laundering schemes. Similarly, government agencies use link analysis to investigate fraud, enhance screening processes, uncover terrorist networks and investigate criminal activities.
At Crime Tech Solutions, we liken the question of how to detect and deter fraud to ‘How do you eat an elephant?’ The answer, of course, is one bite at a time. If big data is the elephant, comprehensive link analysis software is part of the one ‘bite’ at a time. Or should we say ‘byte’.
(NOTE: Crime Tech Solutions is an Austin, TX based provider of investigation software and analytics for commercial and law enforcement groups. We proudly support the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners (ACFE), International Association of Chiefs of Police (IACP), Association of Law Enforcement Intelligence Units (LEIU) and International Association of Crime Analysts (IACA). Our offerings include sophisticated link analysis software, an industry-leading investigation case management solution, and criminal intelligence database management systems.)
What is Crime Analysis?
Posted by Tyler Wood Crime Tech Solutions, your source for investigation software.
The information provided on this page comes primarily from Boba, R. (2008: Pages 3 through 6) Crime Analysis with Crime Mapping. For a full discussion of the crime analysis discipline, refer to the book which can be obtained through www.sagepub.com.
Over the past 20 years, many scholars have developed definitions of crime analysis. Although definitions of crime analysis differ in specifics, they share several common components: all agree that crime analysis supports the mission of the police agency, utilizes systematic methods and information, and provides information to a range of audiences. Thus, the following definition of crime analysis is used as the foundation of this initiative:
Crime analysis is the systematic study of crime and disorder problems as well as other police–related issues—including sociodemographic, spatial, and temporal factors—to assist the police in criminal apprehension, crime and disorder reduction, crime prevention, and evaluation.
Clarification of each aspect of this definition helps to demonstrate the various elements of crime analysis. Generally, to study means to inquire into, investigate, examine closely, and/or scrutinize information. Crime analysis, then, is the focused and systematic examination of crime and disorder problems as well as other police-related issues. Crime analysis is not haphazard or anecdotal; rather, it involves the application of social science data collection procedures, analytical methods, and statistical techniques.
More specifically, crime analysis employs both qualitative and quantitative data and methods. Crime analysts use qualitative data and methods when they examine non-numerical data for the purpose of discovering underlying meanings and patterns of relationships. The qualitative methods specific to crime analysis include field research (such as observing characteristics of locations) and content analysis (such as examining police report narratives). Crime analysts use quantitative data and methods when they conduct statistical analysis of numerical or categorical data. Although much of the work in crime analysis is quantitative, crime analysts use simple statistical methods, such as frequencies, percentages, means, and rates. Typical crime analysis tools include link analysis and crime mapping software.
The central focus of crime analysis is the study of crime (e.g., rape, robbery, and burglary); disorder problems (e.g., noise complaints, burglar alarms, and suspicious activity); and information related to the nature of incidents, offenders, and victims or targets of crime (targets refer to inanimate objects, such as buildings or property). Crime analysts also study other police-related operational issues, such as staffing needs and areas of police service. Even though this discipline is called crime analysis, it actually includes much more than just the examination of crime incidents.
Although many different characteristics of crime and disorder are relevant in crime analysis, the three most important kinds of information that crime analysts use are sociodemographic, spatial, and temporal. Sociodemographic information consists of the personal characteristics of individuals and groups, such as sex, race, income, age, and education. On an individual level, crime analysts use sociodemographic information to search for and identify crime suspects. On a broader level, they use such information to determine the characteristics of groups and how they relate to crime. For example, analysts may use sociodemographic information to answer the question, “Is there a white, male suspect, 30 to 35 years of age, with brown hair and brown eyes, to link to a particular robbery?” or “Can demographic characteristics explain why the people in one group are victimized more often than people in another group in a particular area?”
The spatial nature of crime and other police-related issues is central to understanding the nature of a problem. In recent years, improvements in computer technology and the availability of electronic data have facilitated a larger role for spatial analysis in crime analysis. Visual displays of crime locations (maps) and their relationship to other events and geographic features are essential to understanding the nature of crime and disorder. Recent developments in criminological theory have encouraged crime analysts to focus on geographic patterns of crime, by examining situations in which victims and offenders come together in time and space.
Finally, the temporal nature of crime, disorder, and other police-related issues is a major component of crime analysis. Crime analysts conduct several levels of temporal analysis, including (a) examination of long-term patterns in crime trends over several years, the seasonal nature of crime, and patterns by month; (b) examination of mid-length patterns, such as patterns by day of week and time of day; and (c) examination of short-term patterns, such as patterns by day of the week, time of day, or time between incidents within a particular crime series.
The final part of the crime analysis definition—”to assist the police in criminal apprehension, crime and disorder reduction, crime prevention, and evaluation” generally summarizes the purpose and goals of crime analysis. The primary purpose of crime analysis is to support (i.e., “assist”) the operations of a police department. Without police, crime analysis would not exist as it is defined here.
The first goal of crime analysis is to assist in criminal apprehension, given that this is a fundamental goal of the police. For instance, a detective may be investigating a robbery incident in which the perpetrator used a particular modus operandi (i.e., method of the crime). A crime analyst might assist the detective by searching a database of previous robberies for similar cases.
Another fundamental police goal is to prevent crime through methods other than apprehension. Thus, the second goal of crime analysis is to help identify and analyze crime and disorder problems as well as to develop crime prevention responses for those problems. For example, members of a police department may wish to conduct a residential burglary prevention campaign and would like to target their resources in areas with the largest residential burglary problem. A crime analyst can assist by conducting an analysis of residential burglary to examine how, when, and where the burglaries occurred along with which items were stolen. The analyst can then use this information to develop crime prevention suggestions, (such as closing and locking garage doors) for specific areas.
Many of the problems that police deal with or are asked to solve are not criminal in nature; rather, they are related to quality of life and disorder. Some examples include false burglar alarms, loud noise complaints, traffic control, and neighbor disputes. The third goal of crime analysis stems from the police objective to reduce crime and disorder. Crime analysts can assist police with these efforts by researching and analyzing problems such as suspicious activity, noise complaints, code violations, and trespass warnings. This research can provide officers with information they can use to address these issues before they become more serious criminal problems.
The final goal of crime analysis is to help with the evaluation of police efforts by determining the level of success of programs and initiatives implemented to control and prevent crime and disorder and measuring how effectively police organizations are run. In recent years, local police agencies have become increasingly interested in determining the effectiveness of their crime control and prevention programs and initiatives. For example, an evaluation might be conducted to determine the effectiveness of a two-month burglary surveillance or of a crime prevention program that has sought to implement crime prevention through environmental design (CPTED) principles within several apartment communities. Crime analysts also assist police departments in evaluating internal organizational procedures, such as resource allocation (i.e., how officers are assigned to patrol areas), realignment of geographic boundaries, the forecasting of staffing needs, and the development of performance measures. Police agencies keep such procedures under constant scrutiny in order to ensure that the agencies are running effectively.
In summary, the primary objective of crime analysis is to assist the police in reducing and preventing crime and disorder. Present cutting edge policing strategies, such as hotspots policing, problem-oriented policing, disorder policing, intelligence-led policing, and CompStat management strategies, are centered on directing crime prevention and crime reduction responses based on crime analysis results. Although crime analysis is recognized today as important by both the policing and the academic communities, it is a young discipline and is still being developed. Consequently, it is necessary to provide new and experienced crime analysts with training and assistance that improves their skills and provides them examples of best practices from around the country and the world. http://crimetechsolutions.com
What is Link / Social Network Analysis?
Posted by Crime Tech Solutions
Some linkage data, such as telephone call detail records, may be simple but voluminous, with uniform node and link types and a great deal of regularity. Other data, such as law enforcement data, may be extremely rich and varied, though sparse, with elements possessing many attributes and confidence values that may change over time.
Various techniques are appropriate for distinct problems. For example, heuristic, localized methods might be appropriate for matching known patterns to a network of financial transactions in a criminal investigation. Efficient global search strategies, on the other hand, might be best for finding centrality or severability in a telephone network.
Link analysis can be broken down into two components—link generation, and utilization of the resulting linkage graph.
Link Generation
Link generation is the process of computing the links, link attributes and node attributes. There are several different ways to define links. The different approaches yield very different linkage graphs. A key aspect in defining a link analysis is deciding which representation to use.
Explicit Links
A link may be created between the nodes corresponding to each pair of entities in a transaction. For example, with a call detail record, a link is created between the originating telephone number and the destination telephone number. This is referred to as an explicit link.
Aggregate Links
A single link may be created from multiple transactions. For example, a single link could represent all telephone calls between two parties, and a link attribute might be the number of calls represented. Thus, several explicit links may be collapsed into a single aggregate link.
Inferred Relationships
Links may also be created between pairs of nodes based on inferred strengths of relationships between them. These are sometimes referred to as soft links, association links, or co-occurrence links. Classes of algorithms for these computations include association rules, Bayesian belief networks and context vectors. For example, a link may be created between any pair of nodes whose context vectors lie within a certain radius of one another. Typically, one attribute of such a link is the strength of the relationship it represents. Time is a key feature that offers an opportunity to uncover linkages that might be missed by more typical data analysis approaches. For example, suppose a temporal analysis of wire transfer records indicates that a transfer from account A to person X at one bank is temporally proximate to a transfer from account B to person Y at another bank. This yields an inferred link between accounts A and B. If other aspects of the accounts or transactions are also suspicious, they may be flagged for additional scrutiny for possible money laundering activity.
A specific instance of inferred relationships is identifying two nodes that may actually correspond to the same physical entity, such as a person or an account. Link analysis includes mechanisms for collapsing these to a single node. Typically, the analyst creates rules or selects parameters specifying in which instances to merge nodes in this fashion.
Utilization
Once a linkage graph, including the link and node attributes, has been defined, it can be browsed, searched or used to create variables as inputs to a decision system.
Visualization
In visualizing linking graphs, each node is represented as an icon, and each link is represented as a line or an arrow between two nodes. The node and link attributes may be displayed next to the items or accessed via mouse actions. Different icon types represent different entity types. Similarly, link attributes determine the link representation (line strength, line color, arrowhead, etc.).
Standard graphs include spoke and wheel, peacock, group, hierarchy and mesh. An analytic component of the visualization is the automatic positioning of the nodes on the screen, i.e., the projection of the graph onto a plane. Different algorithms position the nodes based on the strength of the links between nodes or to agglomerate the nodes into groups of the same kind. Once displayed, the user typically has the ability to move nodes, modify node and link attributes, zoom in, collapse, highlight, hide or delete portions of the graph.
Variable Creation
Link analysis can append new fields to existing records or create entirely new data sets for subsequent modeling stages in a decision system. For example, a new variable for a customer might be the total number of email addresses and credit card numbers linked to that customer.
Search
Link analysis query mechanisms include retrieving nodes and links matching specified criteria, such as node and link attributes, as well as search by example to find more nodes that are similar to the specified example node.
A more complex task is similarity search, also called clustering. Here, the objective is to find groups of similar nodes. These may actually be multiple instances of the same physical entity, such as a single individual using multiple accounts in a similar fashion.
Network Analysis
Network analysis is the search for parts of the linkage graph that play particular roles. It is used to build more robust communication networks and to combat organized crime. This exploration revolves around questions such as:
- Which nodes are key or central to the network?
- Which links can be severed or strengthened to most effectively impede or enhance the operation of the network?
- Can the existence of undetected links or nodes be inferred from the known data?
- Are there similarities in the structure of subparts of the network that can indicate an underlying relationship (e.g., modus operandi)?
- What are the relevant sub-networks within a much larger network?
- What data model and level of aggregation best reveal certain types of links and sub-networks?
- What types of structured groups of entities occur in the data set?
Applications
Link analysis tools such as those provided by Crime Tech Solutions are increasingly used in law enforcement investigations, detecting terrorist threats, fraud detection, detecting money laundering, telecommunications network analysis, classifying web pages, analyzing transportation routes, pharmaceuticals research, epidemiology, detecting nuclear proliferation and a host of other specialized applications. For example, in the case of money laundering, the entities might include people, bank accounts and businesses, and the transactions might include wire transfers, checks and cash deposits. Exploring relationships among these different objects helps expose networks of activity, both legal and illegal.
What the heck do Crime Analysts do?
Posted by Crime Tech Solutions – Your source for analytics in the fight against crime and fraud.
NOTE: This great article is property of International Association of Crime Analysts and is posted in it’s original format HERE…
What do Crime Analysts Do?
One: Finding Series, Patterns, Trends, and Hot Spots as They Happen
Crime analysts review all police reports every day with the goal of identifying patterns as they emerge. If a burglar starts targeting drugs stores in your jurisdiction, a crime analyst will let you know on the second incident. If domestic violence becomes a recurring problem in one family, an analyst will catch it. If your city, town, or county faces any emerging problem—youth disorder on a particular street, street robbery hot spots, new trends in fraud and forgery, a pattern of items being stolen from cars—your analyst can identify it and alert you about it as soon as possible.
Analyses of these trends, patterns, and hot spots provide you with the who, what, when, where, how, and why of emerging crime in your community. You can use this information to develop effective tactics and strategies, interceding as soon as possible, preventing victimization, and reducing crime.
Two: Researching and Analyzing Long-Term Problems
Crime analysis isn’t just about immediate patterns and series:analysts also look at the long-term problems that every police department faces. From a park that has been a drug-dealing hot spot for 20 years to a street that has a high number of car accidents to ongoing issues with crime and disorder at budget motels, a crime analyst can take it apart, explore its dimensions, and help the police department come up with long-term solutions.
Three: Providing Information on Demand
How often have you been frustrated getting the information you need from your records management or CAD system? Crime analysts know how to extract data from records systems, ask questions of it, and turn it into useful information. They know how to get data from other sources, and how to work with it. They know how to create charts, maps, graphs, tables, and other visual products.
Whether you need a list of all the incidents of youth violence over five years, or a chart showing trends in OUI arrests, or some statistics on motor vehicle citations, or a map showing an upcoming parade route, or an estimate of how many officers you’ll need in five years if current population trends continue, a trained crime analyst can put it together quickly and clearly.
Four: Developing and Linking Local Intelligence
Since September 11, 2001, we hear a lot about the need for intelligence. But what is it? And what does it have to do with local police departments?
Intelligence describes special information about criminals and criminal organizations: their goals, their activities, their chains of command, how money and goods flow through them, what they’re planning, and so on. Analyzing intelligence data on national and international problems is generally the responsibility of national and international agencies, but local police departments and local analysts play an important role.
First, as information synthesizers, crime analysts often know when local information or intelligence fits with state, national, or international intelligence. If the FBI issues a bulletin stating that terrorists are using forged passports from Belgium, your analyst will know to pay special attention when one of your reports mentions a Belgian passport. If a state agency issues a report on motorcycle gangs, your analyst can integrate that with your own police reports. In the post-September 11 world, you’re bombarded with information from multiple agencies at multiple levels; with a crime analyst, you have someone who can sift through this information and extract what’s relevant to your agency.
Second, your crime analyst can apply criminal intelligence analysis tactics to your local problems. Do you need a link chart showing the relationships between members of a local street gang? Or a carefully-crafted timeline for a court presentation? An analyst is trained in such techniques.
Five: Making Your Department Look Good
A crime analyst makes you and your agency look good to the public and to local government officials. You’re fully informed about a crime pattern before the press calls about it. The analyses, statistics, and charts on your web site and in printed publications convey that you are on top of crime and disorder. And when someone wants some information—whether a town selectman looking for statistics on juvenile liquor parties or a reporter looking for the top accident hot spots—you can provide it completely and quickly.
Crime analysts can also enhance the things you already do. Their desktop publishing skills can breathe new life into your reports, newsletters, and alerts; their graphing and charting skills can spice up your community presentations and budget requests; and their overall analysis and communications skills means that you always have someone on hand to explain crime and disorder—whether in meetings, interviews, or formal presentations—to the members of the community you serve.
