
As a guide for those interested in criminal intelligence systems such as IntelNexus™, Crime Tech Weekly is publishing the following overview of Title 28, Part 23 of the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR 28 Part 23). The policy reads as follows:
CFR 28 PART 23–CRIMINAL INTELLIGENCE SYSTEMS OPERATING POLICIES
1. Purpose.
2. Background.
3. Applicability.
4. Operating principles.
5. Funding guidelines.
6. Monitoring and auditing of grants for the funding of intelligence systems.
1 Purpose.
The purpose of this regulation is to assure that all criminal intelligence systems operating through support under the Omnibus Crime Control and Safe Streets Act of 1968 are utilized in conformance with the privacy and constitutional rights of individuals.
2 Background.
It is recognized that certain criminal activities including but not limited to loan sharking, drug trafficking, trafficking in stolen property, gambling, extortion, smuggling, bribery, and corruption of public officials often involve some degree of regular coordination and permanent organization involving a large number of participants over a broad geographical area. The exposure of such ongoing networks of criminal activity can be aided by the pooling of information about such activities. However, because the collection and exchange of intelligence data necessary to support control of serious criminal activity may represent potential threats to the privacy of individuals to whom such data relates, policy guidelines for Federally funded projects are required.
3 Applicability.
(a) These policy standards are applicable to all criminal intelligence systems operating through support under the Omnibus Crime Control and Safe Streets Act of 1968.
(b) As used in these policies: Criminal Intelligence System or Intelligence System means the arrangements, equipment, facilities, and procedures used for the receipt, storage, interagency exchange or dissemination, and analysis of criminal intelligence information; Inter-jurisdictional Intelligence System means an intelligence system which involves two or more participating agencies representing different governmental units or jurisdictions; Criminal Intelligence Information means data which has been evaluated to determine that it: (i) is relevant to the identification of and the criminal activity engaged in by an individual who or organization which is reasonably suspected of involvement in criminal activity, and (ii) meets criminal intelligence system submission criteria; Participating Agency means an agency of local, county, State, Federal, or other governmental unit which exercises law enforcement or criminal investigation authority and which is authorized to submit and receive criminal intelligence information through an inter-jurisdictional intelligence system. A participating agency may be a member or a nonmember of an inter-jurisdictional intelligence system; Intelligence Project means the organizational unit which operates an intelligence system on behalf of and for the benefit of a single agency or the organization which operates an inter-jurisdictional intelligence system on behalf of a group of participating agencies; and Validation of Information means the procedures governing the periodic review of criminal intelligence information to assure its continuing compliance with system submission criteria established by regulation or program policy.
 4 Operating principles.
4 Operating principles.
(a) A project shall collect and maintain criminal intelligence information concerning an
individual only if there is reasonable suspicion that the individual is involved in criminal conduct or activity and the information is relevant to that criminal conduct or activity.
(b) A project shall not collect or maintain criminal intelligence information about the political, religious or social views, associations, or activities of any individual or any group, association, corporation, business, partnership, or other organization unless such information directly relates to criminal conduct or activity and there is reasonable suspicion that the subject of the information is or may be involved in criminal conduct or activity.
(c) Reasonable Suspicion or Criminal Predicate is established when information exists which establishes sufficient facts to give a trained law enforcement or criminal investigative agency officer, investigator, or employee a basis to believe that there is a reasonable possibility that an individual or organization is involved in a definable criminal activity or enterprise. In an inter-jurisdictional intelligence system, the project is responsible for establishing the existence of reasonable suspicion of criminal activity either through examination of supporting information submitted by a participating agency or by delegation of this responsibility to a properly trained participating agency which is subject to routine inspection and audit procedures established by the project.
(d) A project shall not include in any criminal intelligence system information which has been obtained in violation of any applicable Federal, State, or local law or ordinance. In an inter-jurisdictional intelligence system, the project is responsible for establishing that no information is entered in violation of Federal, State, or local laws, either through examination of supporting information submitted by a participating agency or by delegation of this responsibility to a properly trained participating agency which is subject to routine inspection and audit procedures established by the project.
(e) A project or authorized recipient shall disseminate criminal intelligence information only where there is a need to know and a right to know the information in the performance of a law enforcement activity.
(f) (1) Except as noted in paragraph (f) (2) of this section, a project shall disseminate criminal intelligence information only to law enforcement authorities who shall agree to follow procedures regarding information receipt, maintenance, security, and dissemination which are consistent with these principles. (2) Paragraph (f) (1) of this section shall not limit the dissemination of an assessment of criminal intelligence information to a government official or to any other individual, when necessary, to avoid imminent danger to life or property.

(g) A project maintaining criminal intelligence information shall ensure that administrative, technical, and physical safeguards (including audit trails) are adopted to insure against unauthorized access and against intentional or unintentional damage. A record indicating who has been given information, the reason for release of the information, and the date of each dissemination outside the project shall be kept. Information shall be labeled to indicate levels of sensitivity, levels of confidence, and the identity of submitting agencies and control officials. Each project must establish written definitions for the need to know and right to know standards for dissemination to other agencies as provided in paragraph (e) of this section. The project is responsible for establishing the existence of an inquirer’s need to know and right to know the information being requested either through inquiry or by delegation of this responsibility to a properly trained participating agency which is subject to routine inspection and audit procedures established by the project. Each intelligence project shall assure that the following security requirements are implemented: (1) Where appropriate, projects must adopt effective and technologically advanced computer software and hardware designs to prevent unauthorized access to the information contained in the system; (2) The project must restrict access to its facilities, operating environment and documentation to organizations and personnel authorized by the project; (3) The project must store information in the system in a manner such that it cannot be modified, destroyed, accessed, or purged without authorization; (4) The project must institute procedures to protect criminal intelligence information from unauthorized access, theft, sabotage, fire, flood, or other natural or manmade disaster; (5) The project must promulgate rules and regulations based on good cause for implementing its authority to screen, reject for employment, transfer, or remove personnel authorized to have direct access to the system; and (6) A project may authorize and utilize remote (off-premises) system data bases to the extent that they comply with these security requirements.
(h) All projects shall adopt procedures to assure that all information which is retained by a project has relevancy and importance. Such procedures shall provide for the periodic review of information and the destruction of any information which is misleading, obsolete or otherwise unreliable and shall require that any recipient agencies be advised of such changes which involve errors or corrections. All information retained as a result of this review must reflect the name of the reviewer, date of review and explanation of decision to retain. Information retained in the system must be reviewed and validated for continuing compliance with system submission criteria before the expiration of its retention period, which in no event shall be longer than five (5) years.
(i) If funds awarded under the Act are used to support the operation of an intelligence system, then: (1) No project shall make direct remote terminal access to intelligence information available to system participants, except as specifically approved by the Office of Justice Programs (OJP) based on a determination that the system has adequate policies and procedures in place to insure that it is accessible only to authorized systems users; and (2) A project shall undertake no major modifications to system design without prior grantor agency approval.
 (j) A project shall notify the grantor agency prior to initiation of formal information exchange procedures with any Federal, State, regional, or other information systems not indicated in the grant documents as initially approved at time of award.
(j) A project shall notify the grantor agency prior to initiation of formal information exchange procedures with any Federal, State, regional, or other information systems not indicated in the grant documents as initially approved at time of award.
(k) A project shall make assurances that there will be no purchase or use in the course of the project of any electronic, mechanical, or other device for surveillance purposes that is in violation of the provisions of the Electronic Communications Privacy Act of 1986, Public Law 99-508, 18 U.S.C. 2510-2520, 2701-2709 and 3121-3125, or any applicable State statute related to wiretapping and surveillance.
(l) A project shall make assurances that there will be no harassment or interference with any lawful political activities as part of the intelligence operation.
(m) A project shall adopt sanctions for unauthorized access, utilization, or disclosure of
information contained in the system.
(n) A participating agency of an inter-jurisdictional intelligence system must maintain in its agency files information which documents each submission to the system and supports compliance with project entry criteria. Participating agency files supporting system submissions must be made available for reasonable audit and inspection by project representatives. Project representatives will conduct participating agency inspection and audit in such a manner so as to protect the confidentiality and sensitivity of participating agency intelligence records.
(o) The Attorney General or designee may waive, in whole or in part, the applicability of a particular requirement or requirements contained in this part with respect to a criminal intelligence system, or for a class of submitters or users of such system, upon a clear and convincing showing that such waiver would enhance the collection, maintenance or dissemination of information in the criminal intelligence system, while ensuring that such system would not be utilized in violation of the privacy and constitutional rights of individuals or any applicable state or federal law.
 5 Funding guidelines.
5 Funding guidelines.
The following funding guidelines shall apply to all Crime Control Act funded discretionary assistance awards and Bureau of Justice Assistance (BJA) formula grant program subgrants, a purpose of which is to support the operation of an intelligence system. Intelligence systems shall only be funded where a grantee/subgrantee agrees to adhere to the principles set forth above and the project meets the following criteria:
(a) The proposed collection and exchange of criminal intelligence information has been
coordinated with and will support ongoing or proposed investigatory or prosecutorial activities relating to specific areas of criminal activity.
(b) The areas of criminal activity for which intelligence information is to be utilized represent a significant and recognized threat to the population and: (1) Are either undertaken for the purpose of seeking illegal power or profits or pose a threat to the life and property of citizens; and (2) Involve a significant degree of permanent criminal organization; or (3) Are not limited to one jurisdiction.
(c) The head of a government agency or an individual with general policy making authority who has been expressly delegated such control and supervision by the head of the agency will retain control and supervision of information collection and dissemination for the criminal intelligence system. This official shall certify in writing that he or she takes full responsibility and will be accountable for the information maintained by and disseminated from the system and that the operation of the system will be in compliance with the principles set forth in 23.20.
(d) Where the system is an inter-jurisdictional criminal intelligence system, the governmental agency which exercises control and supervision over the operation of the system shall require that the head of that agency or an individual with general policymaking authority who has been expressly delegated such control and supervision by the head of the agency: (1) assume official responsibility and accountability for actions taken in the name of the joint entity, and (2) certify in writing that the official takes full responsibility and will be accountable for insuring that the information transmitted to the inter-jurisdictional system or to participating agencies will be in compliance with the principles set forth in 23.20. The principles set forth in 0 23.20 shall be made part of the by-laws or operating procedures for that system. Each participating agency, as a condition of participation, must accept in writing those principles which govern the submission, maintenance and dissemination of information included as part of the inter-jurisdictional system.
(e) Intelligence information will be collected, maintained and disseminated primarily for State and local law enforcement efforts, including efforts involving Federal participation.
6 Monitoring and auditing of grants for the funding of intelligence systems.
(a) Awards for the funding of intelligence systems will receive specialized monitoring and audit in accordance with a plan designed to insure compliance with operating principles as set forth in 23.20. The plan shall be approved prior to award of funds.
(b) All such awards shall be subject to a special condition requiring compliance with the
principles set forth in 23.20.
(c) An annual notice will be published by OJP which will indicate the existence and the objective of all systems for the continuing inter-jurisdictional exchange of criminal intelligence information which are subject to the 28 CFR Part 23 Criminal Intelligence Systems Policies.
___________
 Crime Tech Solutions is a leading provider of criminal intelligence database management software for 28 CFR Part 23 compliance. The company also develops Case Closed™ investigation case management software, sophisticated link analysis software, and advanced crime analytics.
Crime Tech Solutions is a leading provider of criminal intelligence database management software for 28 CFR Part 23 compliance. The company also develops Case Closed™ investigation case management software, sophisticated link analysis software, and advanced crime analytics.
 “Task force members can easily add gang members for review, gang events, scars/marks/tattoos, and a host of other important information for the purpose of battling drugs and gangs”, said a Case Closed Software spokesperson.
“Task force members can easily add gang members for review, gang events, scars/marks/tattoos, and a host of other important information for the purpose of battling drugs and gangs”, said a Case Closed Software spokesperson.
 Case Closed Software
Case Closed Software Here’s an excellent, must-read article from Andrew Guthrie Ferguson, a Professor of Law at the
Here’s an excellent, must-read article from Andrew Guthrie Ferguson, a Professor of Law at the 

 Posted by Tyler Wood, Director of Operations at Case Closed Software.
Posted by Tyler Wood, Director of Operations at Case Closed Software.


 Crime Tech Solutions, LLC – a fast growing, vibrant software company based in Leander, TX today announced that a large, coastal city in California has selected them to provide sophisticated
Crime Tech Solutions, LLC – a fast growing, vibrant software company based in Leander, TX today announced that a large, coastal city in California has selected them to provide sophisticated 


 (j) A project shall notify the grantor agency prior to initiation of formal information exchange procedures with any Federal, State, regional, or other information systems not indicated in the grant documents as initially approved at time of award.
(j) A project shall notify the grantor agency prior to initiation of formal information exchange procedures with any Federal, State, regional, or other information systems not indicated in the grant documents as initially approved at time of award. 5 Funding guidelines.
5 Funding guidelines.
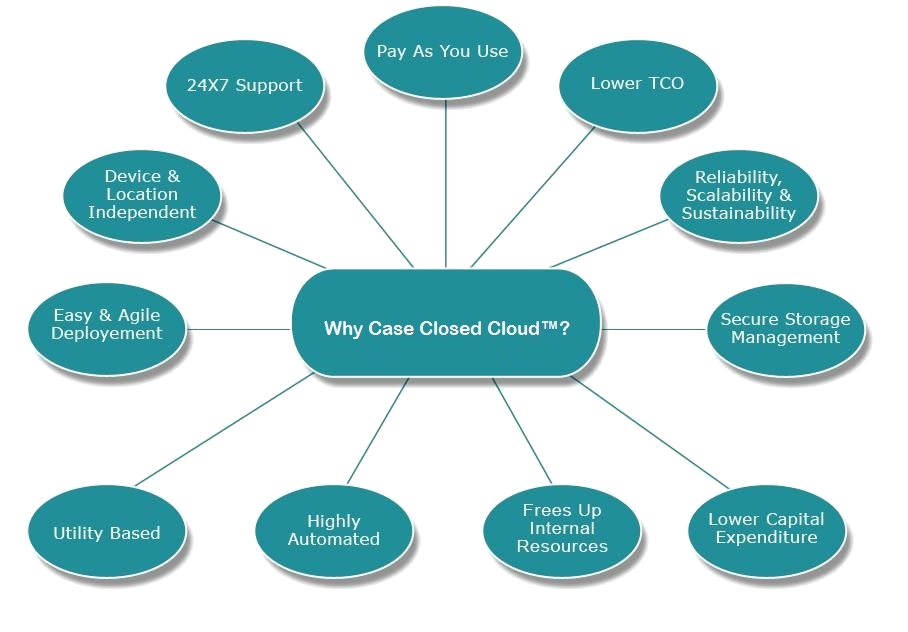
 Cloud computing for law enforcement, in simple terms, refers to software hosted off-agency and available to the user through their internet connection. This type of software-as-a-service, or “SaaS” offers several advantages over software that is hosted locally on the user’s hardware.
Cloud computing for law enforcement, in simple terms, refers to software hosted off-agency and available to the user through their internet connection. This type of software-as-a-service, or “SaaS” offers several advantages over software that is hosted locally on the user’s hardware.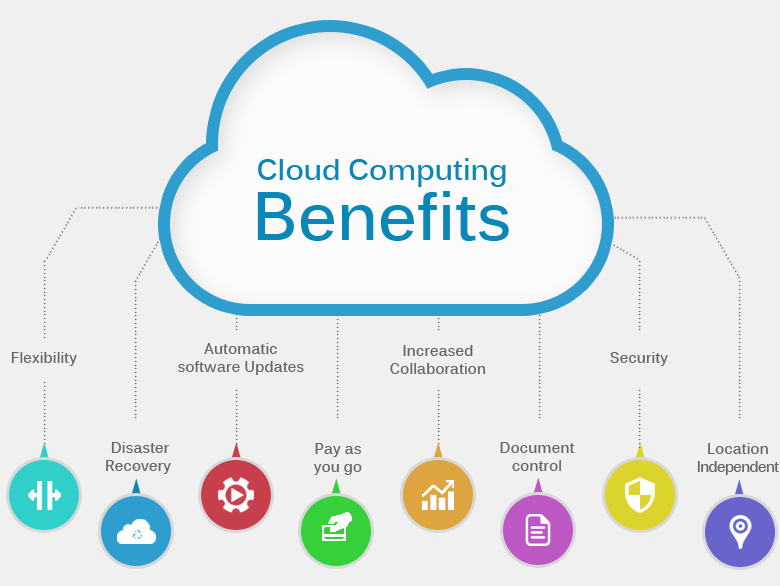 There are some things to look out for. While having software and hardware off-site offers great advantages, it’s important to note that data is hosted off-site as well. It’s important to carefully navigate the terms of use and make certain that the agency is not signing away the rights to important, classified, or proprietary data.
There are some things to look out for. While having software and hardware off-site offers great advantages, it’s important to note that data is hosted off-site as well. It’s important to carefully navigate the terms of use and make certain that the agency is not signing away the rights to important, classified, or proprietary data.