By Tyler Wood, Operations Manager at Crime Tech Solutions.
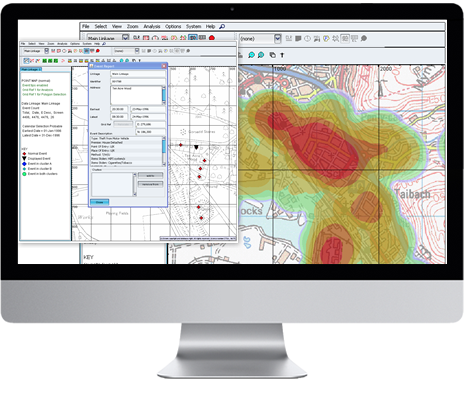
One of the many functions crime analysis performs is the identification of “hot spots”, or geographical areas that seem to be hubs for criminal activity. Identifying these hot spots through best practices in geospatial crime mapping allows law enforcement to focus their efforts in areas that need them most. The trouble that law enforcement and crime analysts have encountered is displacement – the fact that once a hot spot is “cleared”, crime seems to pop up again in a different location. The good news is that the displacement is never 100%, so policing hot spots is important – it’s just not a magic bullet.
To solve this problem, a team at Rutgers University’s School of Criminal Justice set out to develop new methodologies that would result in peaceful outcomes that are built to last instead of merely temporary.
The difference between the old approach and the new approach is stark. Where police and analysts used to focus solely on geographical concentration of crimes, Risk Terrain Modeling examines the factors that contribute to such dense concentrations to begin with. Rutgers team have identified several characteristics of any given geographical location which may attract or generate crime. Their technology takes these characteristics, which include socioeconomic data, physical layout, types of local businesses, etc… and uses them to calculate the likelihood crime occurring in the area. This allows law enforcement to be proactive in the prevention of crime in these areas.
The technique seems to be highly effective. After a trial run in New Haven, CT, police were able to identify sixteen “statistically significant risk factors that underlie violent crime occurrences.” A high percentage of violent crime in New Haven during the test period occurred in locations already identified by the concept of risk terrain modeling. Though the technology is still new, it is clearly showing impressive results already.
Shutting down hot spots is important policing, and risk terrain modeling technology allows analysts and law enforcement officers to be even more proactive in their prevention of crime.
The author, Tyler Wood, is head of operations at Austin, TX based Crime Tech Solutions – an innovator in crime analytics and law enforcement crime-fighting software. The clear price/performance leader for crime fighting software, the company’s offerings include sophisticated Case Closed™ investigative case management and major case management, GangBuster™ gang intelligence software, powerful link analysis software, evidence management, mobile applications for law enforcement, comprehensive crime analytics with mapping and predictive policing, and 28 CFR Part 23 compliant criminal intelligence database management systems.)
Tag Archives: ESRI
CrimeView and TriTech – Concerned? Maybe you should be.
Posted by Tyler Wood, Operations Manager at Crime Tech Solutions
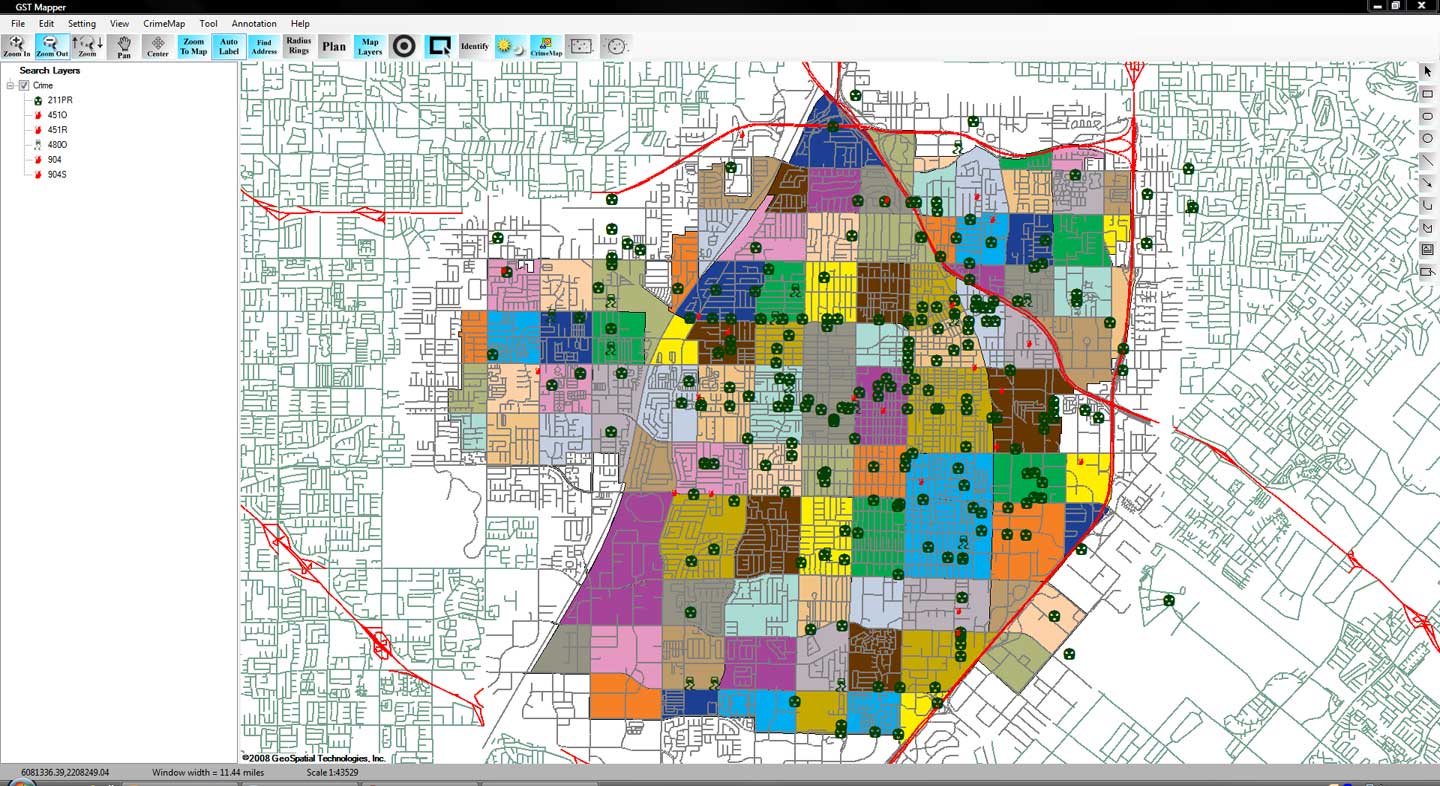
 In the release of a not so well-kept industry secret, Trimble (NASDAQ: TRMB) finally announced this week (February 29, 2016) that it has sold The Omega Group assets to TriTech Software Systems, a leading provider of public safety software. The Omega Group is a large provider of crime mapping software, known for its popular CrimeView™ desktop software and the www.crimemapping.com™ website which allows agencies to present crime statistics to the public in a heat map format.
In the release of a not so well-kept industry secret, Trimble (NASDAQ: TRMB) finally announced this week (February 29, 2016) that it has sold The Omega Group assets to TriTech Software Systems, a leading provider of public safety software. The Omega Group is a large provider of crime mapping software, known for its popular CrimeView™ desktop software and the www.crimemapping.com™ website which allows agencies to present crime statistics to the public in a heat map format.
According to the press release, TriTech intends to grow the acquired business as part of its public safety portfolio. Financial terms of the sale were not disclosed.
So, TriTech continues its acquisition strategy… having already acquired Visionair, Tiburon and Information Management Corp (IMC) over the past decade. Visionair and Tiburon were providers of Records Management Systems (RMS) and Computer Aided Dispatch (CAD) systems for law enforcement.
The previous acquisitions made a great deal of sense for TriTech, as well as the companies being acquired. Most importantly, those acquisitions had no negative affect on the most important group of all – the users and customer base. The acquisition of The Omega Group and CrimeView, however, not so much.
The Omega Group has long been close partners with ESRI®, by far and away the leading developer of GIS mapping technology anywhere. That relationship with ESRI had helped Omega grow into the market force it has become. Of equal importance to that success, however, was the positioning that Omega Group – and their suite of crime map products – were data agnostic and would work with a wide variety of RMS and CAD systems.
Under TriTech’s ownership, however, I don’t see how that ‘impartiality’ continues. TriTech’s previous acquisitions have quickly blended into part of an overall powerful suite of tools – perhaps second to none in the industry – that they market so successfully. Why would we not expect CrimeView et al to follow the same path?
If you’re a current TriTech customer, the acquisition probably has little or no affect on you. Perhaps there’s even an upside as they work to integrate the crime mapping offerings into their other solutions further.
If you’re NOT a TriTech customer, however… well, this is not so good for you. It’s not unreasonable to expect that the company will continue to support third party RMS and CAD implementations for some period of time, but I expect the crime map products to grow in functionality specifically in line with TriTech’s own product set.
Here are our concerns:
- As a user of Omega Group products do you have reason to be concerned that support and development for you will slowly phase out? I’d think so, as TriTech is in the business of selling RMS and CAD solutions.
- If you’re ESRI, can you continue your cozy relationship with a company and product set now owned by a large entity who, by definition, has no interest in growing the non-TriTech base?
- If you’re a competitor to TriTech, can you continue to work with someone who would much prefer to take away your install base than partner with you on the crime map side?
There are low-end, inexpensive competitors to CrimeView but frankly they don’t compare to the functionality and are designed for the very smallest of agencies. CrimeMap from Crime Tech Solutions, on the other hand, is also a partner with ESRI and has a vested interest in remaining agnostic as to the RMS or CAD systems in place. It’s how the company does business.
CrimeMap is a top-tier desktop solution that includes all of the functionality you’d expect, PLUS includes advanced crime analytics, integration with our powerful criminal intelligence database system, and an incredibly useful connectivity to our price/performance leading link analysis solution.
One has to admire TriTech for their continued growth and execution of a solid acquisition strategy. In this acquisition of Omega Group, however, they have put ESRI, end-users, and competitive vendors in an awkward spot.
(NOTE: Crime Tech Solutions is an Austin, TX based provider of crime and fraud analytics software for commercial and law enforcement groups. We proudly support the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners (ACFE), International Association of Chiefs of Police (IACP), Association of Law Enforcement Intelligence Units (LEIU) and International Association of Crime Analysts (IACA). Our offerings include sophisticated link analysis software, comprehensive crime mapping and predictive policing, and criminal intelligence database management systems.)
Best Practices – Geospatial Crime Mapping
Posted by Tyler Wood, Operations Manager at Crime Tech Solutions.

Crime mapping technology is a powerful and valuable tool for law enforcement. The ability to represent crime statistics visually – in a meaningful way – is helping police forces across America to analyze, understand, predict, and even prevent crime. It is, however, important to use caution when using such powerful tools, in order to prevent incorrect analyses of crime statistics that may hinder, rather than help, an investigation.
Specifically, there are a few key mistakes which should be avoided when utilizing this sort of predictive technology.
- Obviously, crime reporting should be thorough and detailed. Crime mapping technology takes a great many factors into consideration when developing a visual analysis of a certain area. The more detailed the input is, the more accurate the predictions and visualizations will be.
- Not every crime occurs at a specific street address. Certain crimes, like personal theft, may not be noticed until hours or even days after they occur, making it difficult to define an exact location at which the crime was committed. Analysts should take care to visualize each location in which it could have occurred.
- When developing a crime map of an area, analysts should take care to split the data between daytime and nighttime hours, as many areas have significantly different rates of crime depending on the time of day. If time is not taken into consideration, data can become skewed and law enforcement can develop a warped picture of the area.
- It is also important for analysts to consider other factors that affect crime reporting within a specific area. For example, petty crimes may be reported less often in lower-income neighborhoods. Care should be taken to consider the demographics and socioeconomic standings of the area being mapped in order to provide more context which can help analysts to more accurately predict and prevent crime.
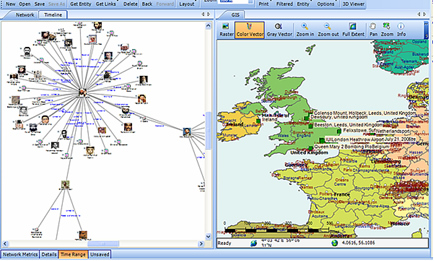 Combining, where possible, the functionality of link analysis into the crime mapping process brings powerful additional functionality. This ability to link, not only statistical, but entity-specific data is a potential game changer.
Combining, where possible, the functionality of link analysis into the crime mapping process brings powerful additional functionality. This ability to link, not only statistical, but entity-specific data is a potential game changer.
The role of crime mapping in the world of law enforcement is gaining popularity. Unfortunately, for many police departments, the cost of a full suite of software from category leader, ESRI is prohibitive. Still, there are options available… notably, CrimeMap Pro from Crime Tech Solutions.
___
(NOTE: Crime Tech Solutions is an Austin, TX based provider of crime and fraud analytics software for commercial and law enforcement groups. We proudly support the Association of Certified Fraud Examiners (ACFE), International Association of Chiefs of Police (IACP), Association of Law Enforcement Intelligence Units (LEIU) and International Association of Crime Analysts (IACA). Our offerings include sophisticated link analysis software, comprehensive crime mapping and predictive policing, and criminal intelligence database management systems.)
Policing in my hometown (Winnipeg) gets smart
Posted by Douglas Wood, Crime Tech Solutions
As a native Winnipeg boy, this article in the Winnipeg Sun caught my attention…
 The government of Manitoba, Canada won’t be making good on its 2011 election pledge to put an extra 50 cops on the streets to combat crime and keep Winnipeg neighborhoods safe.
The government of Manitoba, Canada won’t be making good on its 2011 election pledge to put an extra 50 cops on the streets to combat crime and keep Winnipeg neighborhoods safe.
That may seem odd for a city with the highest violent crime rate in the country. But as policing resources shift away from boots on the ground to more crime-analysis based law enforcement, it’s not more sworn officers the Winnipeg Police Service wants, it’s more resources for so-called smart policing strategies.
“The interest of Winnipeg Police Service is not in officers so much as in crime analysis and smart policing and they have a different approach,” Justice Minister Gord Mackintosh told a legislative committee on Monday. “They do not have an interest in just adding more.” The New Democratic Party promised voters during the last provincial election that it would fund 50 additional officers if re-elected. But four years later, the province has only funded 23 more officers. And there won’t be any new funding for more officers, said Mackintosh.
“The commitment was 50 more officers and we’re now at the equivalent of 23,” said Mackintosh. “The city has requested that the election commitment not be implemented as enunciated during the campaign.” It’s a major shift from years past when provincial parties regularly pledged to put more cops on the street by directly funding the Winnipeg Police Service. The former government was the first to make the promise in 1995 when it promised 40 more police officers for Winnipeg.
The province now directly pays for the salaries and benefits of 172 Winnipeg officers, according to a 2014 report.
And while that funding is expected to continue, the city doesn’t want more money for cops. They want it to help fund other aspects of policing, including more preventative measures, said Mackintosh.
“This is a different approach that is gaining momentum not just here in Winnipeg but in other jurisdictions across the continent,” said Mackintosh. “It’s really about hot spot policing now, it’s about data analysis, looking at the types of offences where they occur, the time of day.” Winnipeg police board chairman Coun. Scott Gillingham confirmed the city isn’t looking for more funding to expand the police complement further. He says police are looking to hire more crime analysts, which can be civilians, not more cops.
“The opportunity and the need would be to focus on preventative measures through things like the smart policing initiative (and) intelligence-led policing,” said Gillingham.
What police also need, though, is more help with the additional workload they’ve taken on as they deal increasingly with mental health patients, Child and Family Services cases and soaring domestic abuse calls.
Police may be moving towards a more data-based approach to law enforcement, but they’ve also become a service of last resort for a growing number of tough social service cases, including tracking down chronic runaway wards of the state on a regular basis.
Which means they’re going to need a lot more support from provincial agencies to pick up some of that slack.
Winnipeg police may not need more boots on the ground. After all, Winnipeg does have the most cops per capita of any Canadian city, and has for some time.
But the province is going to have to figure out how to better manage the social service cases that are landing increasingly at the doorstep of police.
What is Geospatial Crime Mapping?
 Posted by Crime Tech Solutions with information gathered from Wikipedia.
Posted by Crime Tech Solutions with information gathered from Wikipedia.
Here’s a fact: Any understanding of where and why crimes occur can help prevent future crimes.
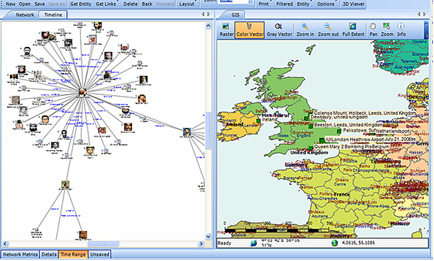
Mapping crime can help law enforcement protect citizens more effectively. Simple maps that display the locations where crimes or concentrations of crimes have occurred can be used to help direct patrols to places they are most needed. Policymakers can use more complex maps to observe trends in criminal activity; such maps can prove invaluable in solving criminal cases. For example, detectives can use maps to better understand the hunting patterns of serial criminals and to hypothesize where these offenders might live.
Products like CrimeMap Pro™ from Crime Tech Solutions are used by analysts in law enforcement agencies to map, visualize, and analyze crime incident patterns. It is a key component of crime analysis and the CompStat policing strategy. Mapping crime, using Geographic Information Systems (GIS), allows crime analysts to identify crime hot spots, along with other trends and patterns.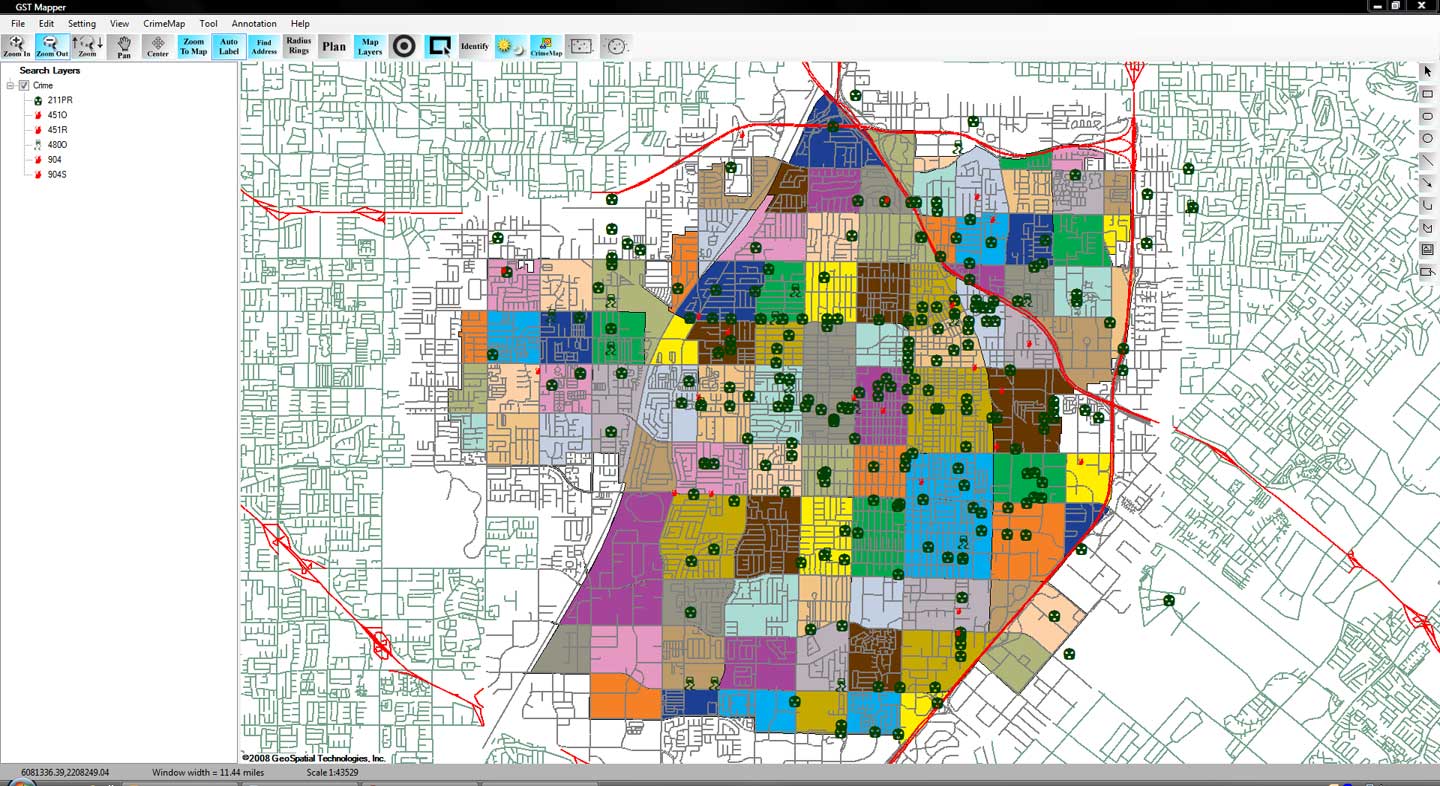
Crime analysts use crime mapping and analysis to help law enforcement management (e.g. the police chief) to make better decisions, target resources, and formulate strategies, as well as for tactical analysis (e.g. crime forecasting, geographic profiling). New York City does this through the CompStat approach, though that way of thinking deals more with the short term. There are other, related approaches with terms including Information-led policing, Intelligence-led policing, Problem-oriented policing, and Community policing. In some law enforcement agencies, crime analysts work in civilian positions, while in other agencies, crime analysts are sworn officers.
From a research and policy perspective, crime mapping is used to understand patterns of incarceration and recidivism, help target resources and programs, evaluate crime prevention or crime reduction programs (e.g. Project Safe Neighborhoods, Weed & Seed and as proposed in Fixing Broken Windows), and further understanding of causes of crime.
The boom of internet technologies, particularly web-based geographic information system (GIS) technologies, is opening new opportunities for use of crime mapping to support crime prevention. Research indicates that the functions provided in web-based crime mapping are less than in most traditional crime mapping software. In conclusion, existing works of web-based crime mapping focus on supporting community policing rather than analytical functions such as pattern analysis and prediction.