 Posted by Douglas Wood.
Posted by Douglas Wood.
Journalist Raj Shekhar had an interesting article in the Times of India this week.
It’s like PreCrime, only four decades early. The “predictive policing” system seen in the Tom Cruise blockbuster Minority Report is now taking shape in Delhi. But instead of the three slime-immersed psychic “Precogs” that system relied on, Delhi Police’s crime prediction will be based on cold, hard data.
Once Enterprise Information Integration Solution or ‘EI2S’—a system that puts petabytes of information from more than a dozen crime databases at police staff’s fingertips—is ready, Delhi Police will be able to implement its ‘Crime Forecast’ plan to predict when and where criminals will strike.
The technology is not as fanciful as it seems at first and is already being tried out in many important cities, including New York, Los Angeles, London and Berlin. Officers associated with the plan say the software will analyze police data for patterns, compare it with other data from jails, courts and other crime-fighting agencies, and alert police to the likely threats. Data will be available not only on the suspects but also their likely victims.
A global tender has been floated for the project and Delhi Police is in talks with various firms for the technology.
According to the article, the system can help pre-empt many situations. For example, a violent clash between two gangs. It can identify individuals who are likely to join gangs or take to crime in an area based on the analyses of their behaviour and network. It can also curb domestic violence by identifying a pattern and predicting the next attack, the article said.
It all boils down to spotting patterns in mountains of data using tremendous computing power. A police document about the plan states that investigators should be able to perform crime series identification, crime trend identification, hot spot analysis and general analysis of criminal profiles. Link analysis will help spot common indicators of a crime by establishing associations and non obvious relationships between entities.
Using neighbourhood analysis, police will be able to understand crime events and the circumstances behind them in a small area as all the crime activity in a neighbourhood will be available for analysis. Criminal cases will be classified into multiple categories to understand what types of crime an area is prone to and the measures needed to curb them. Classification will be done through profiles of victims, suspects, localities and the modus operandi.
Another technique, called proximity analysis, will provide information about criminals, victims, witnesses and other people who are or were within a certain distance of the crime scene. By analyzing demographic and social trends, investigators will be able to understand the changes that have taken place in an area and their impact on criminality.
Network analysis will also be a part of this project to identify the important characteristics and functions of individuals within and outside a network, the network’s strengths and weaknesses and its financial and communication data.
While the system could help fight crime and rid Delhi of its ‘crime capital’ tag, it is bound to raise concerns over privacy and abuse as no predictive system can be foolproof.
Tag Archives: crime analytics
LexisNexis® Acquires BAIR Analytics, Leading Provider of Crime Analytics Solutions for Public Safety
“The acquisition of BAIR Analytics builds on LexisNexis’ commitment to public safety, providing us the ability to combine BAIR Analytic’s analytical capabilities with our public records and linking technology to add context to crime patterns and enhance our ability to identify and locate persons of interest,” said Haywood Talcove, chief executive officer, LexisNexis Special Services, Inc. “The acquisition will be unique in the industry and help public safety officers make better decisions to close cases faster and improve community safety. In an era of constrained budgets, analytics are essential to optimize limited resources and increase overall efficiencies.”
BAIR Analytic’s analytical tools have been used by large and small public safety organizations worldwide for more than 20 years to help reduce and prevent criminal activity.
“Becoming part of LexisNexis will bring new opportunities to expand and build the best possible solutions to help our public safety customers,” said Sean Bair, President, BAIR Analytics. “BAIR Analytic’s ability to help agencies identify, analyze and resolve problems created by criminal offenders will be an exceptional complement to LexisNexis, its proven solutions and vast public records database to offer a more complete view of individuals to accelerate the investigation process.”
About LexisNexis Risk Solutions
LexisNexis Risk Solutions (http://www.lexisnexis.com/risk) is a leader in providing essential information that helps customers across all industries and government assess, predict and manage risk. Combining cutting-edge technology, unique data and advanced analytics, LexisNexis Risk Solutions provides products and services that address evolving client needs in the risk sector while upholding the highest standards of security and privacy. LexisNexis Risk Solutions is part of Reed Elsevier, a world leading provider of professional information solutions.
BAIR Analytics
Established in 1997, BAIR Analytics (http://www.bairanalytics.com) is an analytical software and services company providing innovative tools and subject-matter expertise for public safety, private security, and national security and defense entities. Nearly half of the largest public-safety agencies in the United States use BAIR Analytic’s products & services to fight crime. BAIR Analytic’s current software tools are utilized by police departments, government agencies, and throughout the private sector worldwide to increase and promote smarter, community-oriented preventative policing.
# # #
Media Contact
Stephen Loudermilk
LexisNexis Risk Solutions
678.694.2353
stephen.loudermilk@lexisnexis.com
Using Link Analysis to untangle fraud webs
Posted by Douglas Wood, Editor.
NOTE: This article originally appeared HERE by Jane Antonio. I think it’s a great read…
Link analysis has become an important technique for discovering hidden relationships involved in healthcare fraud. An excellent online source, FierceHealthPayer:AntiFraud, recently spoke to Vincent Boyd Bryant about the value of this tool for payer special investigations units.
A former biometric scientist for the U.S. Department of Defense, Bryant has 30 years of experience in law enforcement and intelligence analysis. He’s an internationally-experienced investigations and forensics expert who’s worked for a leading health insurer on government business fraud and abuse cases.
How does interactive link analysis help insurers prevent healthcare fraud? Can you share an example of how the tool works?
One thing criminals do best is hide pots of money in different places. As a small criminal operation becomes successful, it will often expand its revenue streams through associated businesses. Link analysis is about trying to figure out where all those different baskets of revenue may be. Insurers are drowning in a sea of theft. Here’s where link analysis becomes beneficial. Once insurers discover a small basket of money lost to a criminal enterprise, then serious research needs to go into finding out who owns the company, who they’re associated with, what kinds of business they’re doing and if there are claims associated with it.
You may find a clinic, for example, connected to and working near a pharmacy, a medical equipment supplier, a home healthcare services provider and a construction company. Diving into those companies and what they do, you find that they’re serving older patients for whom multiple claims from many providers exist. The construction company may be building wheelchair ramps on homes. And you may find that the providers are claiming payment for dead people. Overall, using this tool requires significant curiosity and a willingness to look beyond the obvious.
Any investigation consists of aggregating facts, generating impressions and creating a theory about what happened. Then you work to confirm or disconfirm your theory. It’s important to have tools that let you take large masses of facts and visualize them in ways that cue you to look closer.
Let’s say you investigate a large medical practice and interview “Doctor Jones.” The day after the interview, you learn through link analysis that he transferred $11 million from his primary bank account to the Cayman Islands. And in looking at Dr. Jones’ phone records, you see he called six people, each of whom was the head of another individual practice on whose board Dr. Jones sits. Now the investigation expands, since the timing of those phone calls was contemporaneous to the money taking flight.
Why are tight clusters of similar entities possible indicators of fraud, waste or abuse?
Bryant: When you find a business engaged in dishonest practices and see its different relationships with providers working out of the same building, this gives rise to reasonable suspicion. The case merits a closer look. Examining claims and talking to members served by those companies will give you an indication of how legitimate the operation is.
What are the advantages of link analysis to payer special investigation units, and how are SIUs using its results?
Bryant: Link analysis can define relationships through data insurers haven’t always had, data that traditionally belonged to law enforcement.
Link analysis results in a visual reference that can take many forms: It can look like a family tree, an organizational chart or a time line. This reference helps investigators assess large masses of data for clustering and helps them arrive at a conclusion more rapidly.
Using link analysis, an investigator can dump in large amounts of data–such as patient lists from multiple practices–and see who’s serving the same patient. This can identify those who doctor shop for pain medication, for example. Link analysis can chart where this person was and when, showing the total amount of medication prescribed and giving you an idea of how the person is operating.
What types of data does link analysis integrate?
Bryant: Any type of data that can be sorted and tied together can be loaded into the tool. Examples include telephone records, addresses, vehicle information, corporate records that list individuals serving on boards and banking and financial information. Larger supporting documents can be loaded and linked to the charts, making cases easier to present to a jury.
Linked analysis can pull in data from state government agencies, county tax records or police records from state departments of correction and make those available in one bucket. In most cases, this is more efficient than the hours of labor needed to dig up these types of public records through site visits.
Is there anything else payers should know about link analysis that wasn’t covered in the above questions?
Bryant: The critical thing is remembering that you don’t know what you don’t know. If a provider or member is stealing from the plan in what looks like dribs and drabs, insurers may never discover the true extent of the losses. But if–as a part of any fraud allegation that arises–you look at what and who is associated with the subject of the complaint, what started as a $100,000 questionable claims allegation can expose millions of dollars in inappropriate billings spread across different entities.
Part Two: Major Investigation Analytics – Big Data and Smart Data
Posted by Douglas Wood, Editor.
As regular readers of this blog know, I spend a great deal of time writing about the use of technology in the fight against crime – financial and otherwise. In Part One of this series, I overviewed the concept of Major Investigation Analytics and Investigative Case Management.
I also overviewed the major providers of this software technology – Palantir Technologies, Case Closed Software, and Visallo. The latter two recently became strategic partners, in fact.
The major case for major case management (pun intended) was driven home at a recent crime and investigation conference in New York. Full Disclosure: I attended the conference for educational purposes as part of my role at Crime Tech Weekly. Throughout the three day conference, speaker after speaker talked about making sense of data. I think if I’d have heard the term ‘big data’ one more time I’d have gone insane. Nevertheless, that was the topic du jour as you can imagine, and the 3 V’s of big data – volume, variety, and velocity – remain a front and center topic for the vendor community serving the investigation market.
According to one report, 96% of everything we do in life – personal or at work – generates data. That statement probably best sums up how big ‘big data’ is. Unfortunately, there was very little discussion about how big data can help investigate major crimes. There was a lot of talk about analytics, for sure, but there was a noticeable lack of ‘meat on the bone’ when it came to major investigation analytics.
Nobody has ever yelled out “Help, I’ve been attacked. Someone call the big data!”. That’s because big data doesn’t, in and by itself, do anything. Once you can move ‘big data’ into ‘smart data’, however, you have an opportunity to investigate and adjudicate crime. To me, smart data (in the context of investigations) is a subset of an investigator’s ability to:
- Quickly triage a threat (or case) using only those bits of data that are most immediately relevant
- Understand the larger scope of the crime through experience and crime analytics, and
- Manage that case through intelligence-led analytics and investigative case management, data sharing, link exploration, text analytics, and so on.
Connecting the dots, as they say. From an investigation perspective, however, connecting dots can be daunting. In the children’s game, there is a defined starting point and a set of rules. We simply need to follow the instructions and the puzzle is solved. Not so in the world of the investigator. The ‘dots’ are not as easy to find. It can be like looking for a needle in a haystack, but the needle is actually broken into pieces and spread across ten haystacks.
Big data brings those haystacks together, but only smart data finds the needles… and therein lies the true value of major investigation analytics.
Part 2: Investigating the Investigations – X Marks the Spot
Posted by Douglas Wood, Editor. http://www.linkedin.com/in/dougwood
Part One of this series is HERE.
Most of the financial crimes investigators I know live in a world where they dream of moving things from their Inbox to their Outbox. Oh, like everyone else, they also dream about winning the lottery, flying without wings, and being naked in public. But in terms of the important roles they perform within both public and private sectors, there is simply Investigating (Inbox) and Adjudication (Outbox). Getting there requires a unique blend of their own capabilities, the availability of data, and the technology that allows them to operate. In the diagram below, ‘X‘ marks the spot where crimes are moved from the Inbox to the Outbox. Without any of those three components, an investigation becomes exponentially more difficult to conclude.
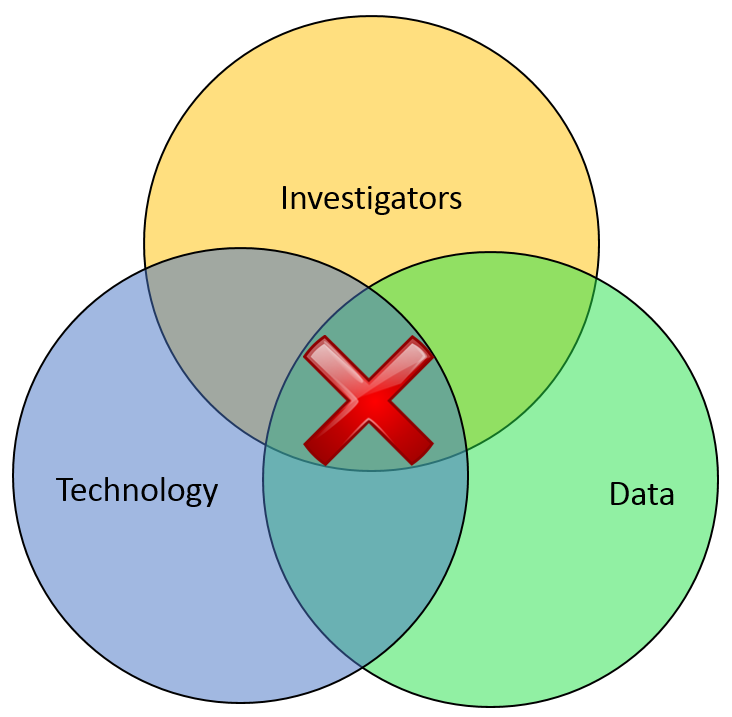
In part one of this article two weeks ago, I wrote about the Investigation Management & Adjudication (IMA) side of financial crimes investigations. I coined that term to call out what is arguably the most integral component of any enterprise fraud management (EFM) ecosystem. The original EFM overview is here.
“The job is almost unrecognizable to those who once used rotary phones in smoke filled offices…
Twenty years ago, IMA was based primarily upon human eyes. Yes, there were technology tools available such as Wordperfect charts and Lotus 1-2-3 spreadsheets, but ultimately it was the investigator who was tasked with finding interesting connections across an array of data elements including handwritten briefs, telephone bills, lists of suspect information, and discussions with other investigators. The job got done, though. Things moved from the Inbox to the Outbox, arrests were made and prosecutions were successful. Kudos, therefore, to all of the investigators who worked in this environment.
Fast forward to today, and the investigator’s world is dramatically different. The job is the same, of course, but the tools and mass availability of data has made the job almost unrecognizable to those who once used rotary phones in smoke filled offices. Organizations began building enterprise data warehouses designed to provide a single version of the truth. Identity Resolution technology was implemented to help investigators recognize similarities between entities in that data warehouse. And today, powerful new IMA tools are allowing easy ingestion of that data, improved methods for securely sharing across jurisdictions, automated link discovery, non-obvious relationship detection, and interactive visualization tools, and -importantly – packaged e-briefs which can be understood and used by law enforcement, prosecutors, or adjudication experts.
“Without any of these components, everything risks falling to the outhouse…
With all these new technologies, surely the job of the Investigator is becoming easier? Not so fast.
IMA tools – and other EFM tools – do nothing by themselves. The data – big data – does nothing by itself. It just sits there. The best investigators – without tools or data – are rendered impotent. Only the combination of skilled, trained investigators using the best IMA tools to analyze the most useful data available results in moving things from the Inbox to the Outbox. Without any of these components… everything eventually risks falling to the Outhouse.
Kudos again, Mr. and Mrs. Investigator. You’ll always be at the heart of every investigation. Here’s hoping you solve for X every day.