In the first chapters of this series, Managing Major Cases, I focused on what defines a major case… and what are some of the unique problems associated with different major case ‘types’. For reference, you can find our previous chapters below:
Managing Major Cases: Part One
Managing Major Cases: Part Two
Managing Major Cases: Part Three
In this chapter, I want to overview the operational structure of Major Case Management.
The Command Triangle
Many Commonwealth countries (and some larger US jurisdictions) define Major Case Management roles within what’s called a “Command Triangle”. Specifically, per the diagram below, jurisdictions within countries such as Great Britain, and Canada define three (3) primary roles – a Major Case Manager who is responsible for the effective governance of the investigation, a Primary Investigator who reports to the Major Case Manager, and a File Coordinator who is responsible for coordination for internal communication and case file management.
Let’s take a look at the responsibilities of each role:
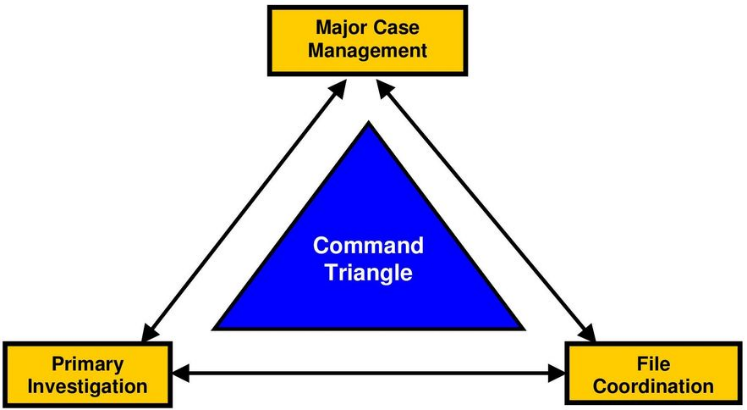
As part of this Command Triangle, the Major Case Manager is accountable for the overall investigation. He or She determines investigation strategies, identifies and manages investigative resources, conducts case reviews, and all other high-level management functions.
The Primary Investigator typically reports to the Major Case Manager and is responsible for tasks including preparation of the case file for status meetings, ensuring that assignments are completed in a timely fashion, identification of resources required for the investigation, and report any major case updates to the Major Case Manager.
Also reporting to the Major Case Manager is the File Coordinator. Their job is also multi-faceted, and includes tasks such as scrutinizing the documents created during the process of the investigation to ensure the completeness and quality, ensuring that tips and leads are assigned and managed, ensuring the security of the case file(s), ensuring that all case actions are logged into the investigative case management software, and more.
Within these three roles are any number of supervisors and line staff that perform interviews, collect evidence, communicate with the media, and so on. Not to beat a dead horse here, but I’ll point out again that all of these roles may be performed by just a few people in some jurisdictions.
The Command Triangle vs. The Major Case Framework
I believe in The Command Triangle model but also strongly support a more US-centric model – The Major Case Framework. Perhaps the differences are subtle, but a Triangle is a hard shape with defined lengths and known, predictable angles. A Framework, however, is just that – a frame which, by nature, allows for additional flexibility than a hard shape. A frame is designed to support a structure, not confine it.
It’s this flexibility that makes the Major Case Framework ideally suited for the U.S. market. By that, I mean there are 200 or 300 law enforcement agencies in Canada, the majority of which have dozens or hundreds of officers. Down here, there are over 18,000 law enforcement agencies ranging in size from NYPD (More than 50,000 Officers) to Frenchtown, New Jersey (3 Officers). This type of variance requires the flexibility of a framework.
So, what is the Major Case Framework?
As noted in discussing The Command Triangle, managing major cases generally consists of organizational groups that perform different, but equally important, roles. The Major Case Framework, however, better recognizes the true nature of investigations by acknowledging from the outset that many, and sometimes all, of the roles are performed by only a small number of individuals and that role flexibility is part of day to day investigation work.
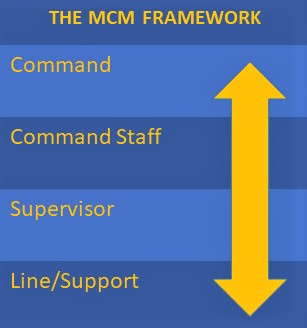
There are four main organizational groups within the Major Case Framework. They are defined as:
- Command: Personnel who establish standard operating procedures, guidelines, and policies, along with the direction that ensures departmental compliance with mandates and laws. The responsibility for the specific directions that a MCM Team takes falls into the hands of those in the Command role. Some examples of Command roles include Chiefs of Police, Sheriffs, Task Force Commanders, and Commissioners.
- Command Staff: Personnel who are charged with the high-level implementation of the policies driven by those in the Command role. CID unit heads, divisional Captains, and task force Directors are examples of the roles that fall into this group.
- Supervisor: Personnel who manage, control, and direct the actual resources of the MCM Team. There are any number of ranks that fill this important role, including Lieutenants and Sergeants, but – in general – the Supervisor is the individual who holds responsibility for the actual control of the personnel involved in the daily activities of the investigation.
- Line/Support: Personnel who perform the day to day tasks related to the investigation. These are the Detectives, Investigators, Technicians, Deputies, Analysts, and a host of other titles that are working the investigation at the ground level. The success of this organizational group.
As noted in the MCM Framework diagram, in many organizations ‘Commanders’ will find themselves performing Line/Support functions, and Supervisors will often find themselves doing the roles defined in ‘Command Staff’. American Law Enforcement, particularly small and medium-sized agencies and task forces, require the flexibility of the framework in order to succeed.
It is important that any agency’s case management systems and processes allow for the flexibility of both the Command Triangle and the Command Framework.
 Douglas Wood is CEO of Crime Technology Solutions | Case Closed Software, a leading provider of serious investigation software to law enforcement, state bureaus, DA offices, and other investigative units. Doug can be reached directly HERE.
Douglas Wood is CEO of Crime Technology Solutions | Case Closed Software, a leading provider of serious investigation software to law enforcement, state bureaus, DA offices, and other investigative units. Doug can be reached directly HERE.



 Douglas Wood is CEO of
Douglas Wood is CEO of